In the world of macOS, power users and developers often seek tools that enhance their efficiency and expand the capabilities of their systems. Homebrew stands out as one of these essential tools. Often referred to as “the missing package manager for macOS,” Homebrew simplifies the installation of software and developer tools on a Mac. This guide will walk you through the process of installing Homebrew on your macOS, ensuring a smooth and successful setup.
What is Homebrew?
Homebrew is an open-source package manager for macOS. It allows users to easily install, update, and manage software packages on their Mac. Unlike the Mac App Store, Homebrew provides access to a vast repository of open-source and command-line tools that are not available through conventional channels.
Requirements
Before installing Homebrew, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- macOS operating system (preferably the latest version).
- Command Line Tools for Xcode: Homebrew requires these tools which include compilers and other development utilities.
Step 1: Install Command Line Tools for Xcode
If you haven’t already installed the Command Line Tools for Xcode, follow these steps:
- Open the Terminal app (found in /Applications/Utilities/).
- Enter the following command and press Enter:
xcode-select --install - A software update popup window will appear. Click “Install” to begin the installation.
Step 2: Install Homebrew
With the Command Line Tools installed, you can now install Homebrew:
- In the Terminal, paste the following command (this can be found on the Homebrew website):
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)" - Press Enter to execute the command. You may be prompted to enter your macOS user password.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
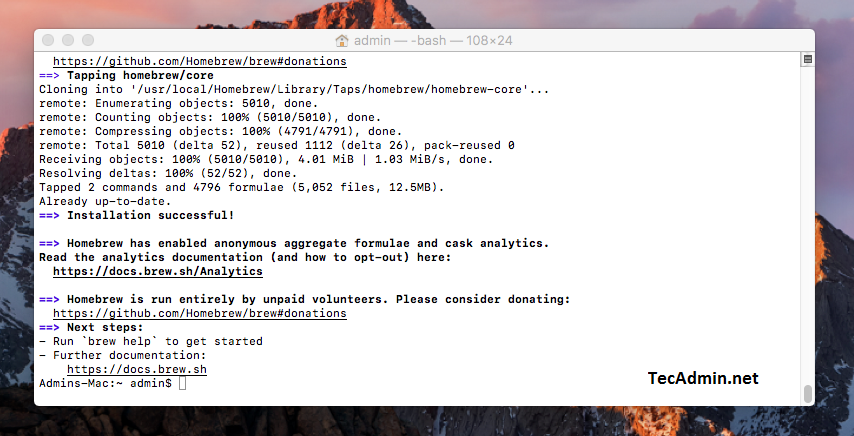
Installing homebrew on macOS - Upon successful installation, Homebrew will provide you with some useful information, including the installation path and how to get started with Homebrew commands.
Step 3: Configure Homebrew for Zsh/Bash
After installing Homebrew, configure it for your shell (Zsh or Bash):
- For Zsh:
Zsh is the default shell on macOS Catalina and later. Add Homebrew to your
~/.zshrcfile by typing:echo 'eval "$(/opt/homebrew/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> ~/.zshrcsource ~/.zshrc - For Bash:
If you’re using Bash, add Homebrew to your
~/.bash_profile:echo 'eval "$(/opt/homebrew/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> ~/.bash_profilesource ~/.bash_profile
Step 4: Verify the Installation
After installation, it’s essential to verify that Homebrew is correctly installed:
- In the Terminal, type:
brew doctor - If you see “Your system is ready to brew”, Homebrew is installed and working correctly.
Step 5: Using Homebrew
Homebrew serves as a tool for installing, updating, and removing software packages on your system. Here is a few useful examples:
- Update Homebrew
It’s recommended to update Homebrew regularly to get the most recent versions of packages. Execute the following command to update Homebrew:
brew update - Install Packages
To install a specific package via Homebrew, utilize the command
brew installfollowed by the name of the package.brew install [package_name]For instance, to install Git, the version control system, you would type:
brew install git - Uninstall Packages
If you need to remove a package, use
brew uninstallfollowed by the name of the package:brew uninstall packageName - Search for Packages
For finding available packages in Homebrew, the command is
brew search:brew search [searchTerm] - List Installed Packages
To view a list of all the packages you have installed through Homebrew, simply run:
brew list
Conclusion
Installing Homebrew on your macOS is a straightforward process that opens up a world of possibilities for software management and development tools. With Homebrew, you have access to a vast repository of applications and utilities, making your macOS experience more powerful and efficient. Remember to periodically run brew update and brew upgrade to keep your packages up to date.
In addition to the basic commands discussed in this article, Homebrew offers many other features and options. For more information and to explore further, visit the official Homebrew documentation at https://docs.brew.sh/.
With Homebrew installed, you can now effortlessly install various development tools, libraries, and services such as Node.js, Python, MySQL, and more. By leveraging Homebrew’s capabilities, you can streamline your development workflow and enhance your productivity as a developer on macOS.


2 Comments
j’arrive pas voici lerreur
pc85:~ felicite$ curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install
#!/System/Library/Frameworks/Ruby.framework/Versions/Current/usr/bin/ruby
# This script installs to /usr/local only. To install elsewhere you can just
# untar https://github.com/Homebrew/brew/tarball/master anywhere you like or
# change the value of HOMEBREW_PREFIX.
HOMEBREW_PREFIX = “/usr/local”.freeze
HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY = “/usr/local/Homebrew”.freeze
HOMEBREW_CACHE = “#{ENV[“HOME”]}/Library/Caches/Homebrew”.freeze
HOMEBREW_OLD_CACHE = “/Library/Caches/Homebrew”.freeze
BREW_REPO = “https://github.com/Homebrew/brew”.freeze
CORE_TAP_REPO = “https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew-core”.freeze
# no analytics during installation
ENV[“HOMEBREW_NO_ANALYTICS_THIS_RUN”] = “1”
ENV[“HOMEBREW_NO_ANALYTICS_MESSAGE_OUTPUT”] = “1”
module Tty
module_function
def blue
bold 34
end
def red
bold 31
end
def reset
escape 0
end
def bold(n = 39)
escape “1;#{n}”
end
def underline
escape “4;39”
end
def escape(n)
“\033[#{n}m” if STDOUT.tty?
end
end
class Array
def shell_s
cp = dup
first = cp.shift
cp.map { |arg| arg.gsub ” “, “\\ ” }.unshift(first).join(” “)
end
end
def ohai(*args)
puts “#{Tty.blue}==>#{Tty.bold} #{args.shell_s}#{Tty.reset}”
end
def warn(warning)
puts “#{Tty.red}Warning#{Tty.reset}: #{warning.chomp}”
end
def system(*args)
abort “Failed during: #{args.shell_s}” unless Kernel.system(*args)
end
def sudo(*args)
args.unshift(“-A”) unless ENV[“SUDO_ASKPASS”].nil?
ohai “/usr/bin/sudo”, *args
system “/usr/bin/sudo”, *args
end
def getc
system “/bin/stty raw -echo”
if STDIN.respond_to?(:getbyte)
STDIN.getbyte
else
STDIN.getc
end
ensure
system “/bin/stty -raw echo”
end
def wait_for_user
puts
puts “Press RETURN to continue or any other key to abort”
c = getc
# we test for \r and \n because some stuff does \r instead
abort unless (c == 13) || (c == 10)
end
class Version
include Comparable
attr_reader :parts
def initialize(str)
@parts = str.split(“.”).map { |p| p.to_i }
end
def (other)
parts self.class.new(other).parts
end
end
def force_curl?
ARGV.include?(“–force-curl”)
end
def macos_version
@macos_version ||= Version.new(`/usr/bin/sw_vers -productVersion`.chomp[/10\.\d+/])
end
def should_install_command_line_tools?
return false if force_curl?
return false if macos_version /dev/null`.chomp
exe if $? && $?.success? && !exe.empty? && File.executable?(exe)
end
return unless @git
# Github only supports HTTPS fetches on 1.7.10 or later:
# https://help.github.com/articles/https-cloning-errors
`#{@git} –version` =~ /git version (\d\.\d+\.\d+)/
return if $1.nil?
return if Version.new($1) > 6) & 07
# g = (mode >> 3) & 07
# o = (mode >> 0) & 07
mode != 0755
end
def chmod?(d)
File.exist?(d) && !(File.readable?(d) && File.writable?(d) && File.executable?(d))
end
def chown?(d)
!File.owned?(d)
end
def chgrp?(d)
!File.grpowned?(d)
end
# Invalidate sudo timestamp before exiting (if it wasn’t active before).
Kernel.system “/usr/bin/sudo -n -v 2>/dev/null”
at_exit { Kernel.system “/usr/bin/sudo”, “-k” } unless $?.success?
# The block form of Dir.chdir fails later if Dir.CWD doesn’t exist which I
# guess is fair enough. Also sudo prints a warning message for no good reason
Dir.chdir “/usr”
####################################################################### script
abort “See Linuxbrew: http://linuxbrew.sh/” if RUBY_PLATFORM.to_s.downcase.include?(“linux”)
abort “Mac OS X too old, see: https://github.com/mistydemeo/tigerbrew” if macos_version < "10.5"
abort "Don't run this as root!" if Process.uid.zero?
abort <<-EOABORT unless `dsmemberutil checkmembership -U "#{ENV["USER"]}" -G admin`.include? "user is a member"
This script requires the user #{ENV["USER"]} to be an Administrator.
EOABORT
# Tests will fail if the prefix exists, but we don't have execution
# permissions. Abort in this case.
abort <<-EOABORT if File.directory?(HOMEBREW_PREFIX) && (!File.executable? HOMEBREW_PREFIX)
The Homebrew prefix, #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}, exists but is not searchable. If this is
not intentional, please restore the default permissions and try running the
installer again:
sudo chmod 775 #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}
EOABORT
ohai "This script will install:"
puts "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin/brew"
puts "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/doc/homebrew"
puts "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/man/man1/brew.1"
puts "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/zsh/site-functions/_brew"
puts "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/etc/bash_completion.d/brew"
puts HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY.to_s
group_chmods = %w[ bin bin/brew etc Frameworks include lib sbin share var
etc/bash_completion.d lib/pkgconfig var/log
share/aclocal share/doc share/info share/locale share/man
share/man/man1 share/man/man2 share/man/man3 share/man/man4
share/man/man5 share/man/man6 share/man/man7 share/man/man8].
map { |d| File.join(HOMEBREW_PREFIX, d) }.
select { |d| chmod?(d) }
# zsh refuses to read from these directories if group writable
zsh_dirs = %w[share/zsh share/zsh/site-functions].
map { |d| File.join(HOMEBREW_PREFIX, d) }
user_chmods = zsh_dirs.select { |d| user_only_chmod?(d) }
chmods = group_chmods + user_chmods
chowns = chmods.select { |d| chown?(d) }
chgrps = chmods.select { |d| chgrp?(d) }
mkdirs = %w[Cellar Homebrew Frameworks bin etc include lib opt sbin share share/zsh share/zsh/site-functions var].
map { |d| File.join(HOMEBREW_PREFIX, d) }.
reject { |d| File.directory?(d) }
unless group_chmods.empty?
ohai "The following existing directories will be made group writable:"
puts(*group_chmods)
end
unless user_chmods.empty?
ohai "The following existing directories will be made writable by user only:"
puts(*user_chmods)
end
unless chowns.empty?
ohai "The following existing directories will have their owner set to #{Tty.underline}#{ENV["USER"]}#{Tty.reset}:"
puts(*chowns)
end
unless chgrps.empty?
ohai "The following existing directories will have their group set to #{Tty.underline}admin#{Tty.reset}:"
puts(*chgrps)
end
unless mkdirs.empty?
ohai "The following new directories will be created:"
puts(*mkdirs)
end
if should_install_command_line_tools?
ohai "The Xcode Command Line Tools will be installed."
end
wait_for_user if STDIN.tty? && !ENV["TRAVIS"]
if File.directory? HOMEBREW_PREFIX
sudo "/bin/chmod", "u+rwx", *chmods unless chmods.empty?
sudo "/bin/chmod", "g+rwx", *group_chmods unless group_chmods.empty?
sudo "/bin/chmod", "755", *user_chmods unless user_chmods.empty?
sudo "/usr/sbin/chown", ENV["USER"], *chowns unless chowns.empty?
sudo "/usr/bin/chgrp", "admin", *chgrps unless chgrps.empty?
else
sudo "/bin/mkdir", "-p", HOMEBREW_PREFIX
sudo "/usr/sbin/chown", "root:wheel", HOMEBREW_PREFIX
end
unless mkdirs.empty?
sudo "/bin/mkdir", "-p", *mkdirs
sudo "/bin/chmod", "g+rwx", *mkdirs
sudo "/bin/chmod", "755", *zsh_dirs
sudo "/usr/sbin/chown", ENV["USER"], *mkdirs
sudo "/usr/bin/chgrp", "admin", *mkdirs
end
[HOMEBREW_CACHE, HOMEBREW_OLD_CACHE].each do |cache|
sudo "/bin/mkdir", "-p", cache unless File.directory? cache
sudo "/bin/chmod", "g+rwx", cache if chmod? cache
sudo "/usr/sbin/chown", ENV["USER"], cache if chown? cache
sudo "/usr/bin/chgrp", "admin", cache if chgrp? cache
end
if should_install_command_line_tools?
ohai "Searching online for the Command Line Tools"
# This temporary file prompts the 'softwareupdate' utility to list the Command Line Tools
clt_placeholder = "/tmp/.com.apple.dt.CommandLineTools.installondemand.in-progress"
sudo "/usr/bin/touch", clt_placeholder
clt_label = `softwareupdate -l | grep -B 1 -E "Command Line (Developer|Tools)" | awk -F"*" '/^ +\\*/ {print $2}' | sed 's/^ *//' | tail -n1`.chomp
ohai "Installing #{clt_label}"
sudo "/usr/sbin/softwareupdate", "-i", clt_label
sudo "/bin/rm", "-f", clt_placeholder
sudo "/usr/bin/xcode-select", "–switch", "/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools"
end
# Headless install may have failed, so fallback to original 'xcode-select' method
if should_install_command_line_tools? && STDIN.tty?
ohai "Installing the Command Line Tools (expect a GUI popup):"
sudo "/usr/bin/xcode-select", "–install"
puts "Press any key when the installation has completed."
getc
sudo "/usr/bin/xcode-select", "–switch", "/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools"
end
abort <&1` =~ /license/ && !$?.success?
You have not agreed to the Xcode license.
Before running the installer again please agree to the license by opening
Xcode.app or running:
sudo xcodebuild -license
EOABORT
ohai “Downloading and installing Homebrew…”
Dir.chdir HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY do
if git
# we do it in four steps to avoid merge errors when reinstalling
system git, “init”, “-q”
# “git remote add” will fail if the remote is defined in the global config
system git, “config”, “remote.origin.url”, BREW_REPO
system git, “config”, “remote.origin.fetch”, “+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*”
# ensure we don’t munge line endings on checkout
system git, “config”, “core.autocrlf”, “false”
args = git, “fetch”, “origin”, “master:refs/remotes/origin/master”,
“–tags”, “–force”
system(*args)
system git, “reset”, “–hard”, “origin/master”
system “ln”, “-sf”, “#{HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY}/bin/brew”, “#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin/brew”
system “#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin/brew”, “update”, “–force”
else
# -m to stop tar erroring out if it can’t modify the mtime for root owned directories
# pipefail to cause the exit status from curl to propagate if it fails
curl_flags = “fsSL”
curl_flags += “k” if macos_version < "10.6"
core_tap = "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/Homebrew/Library/Taps/homebrew/homebrew-core"
system "/bin/bash -o pipefail -c '/usr/bin/curl -#{curl_flags} #{BREW_REPO}/tarball/master | /usr/bin/tar xz -m –strip 1'"
system "ln", "-sf", "#{HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY}/bin/brew", "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin/brew"
system "/bin/mkdir", "-p", core_tap
Dir.chdir core_tap do
system "/bin/bash -o pipefail -c '/usr/bin/curl -#{curl_flags} #{CORE_TAP_REPO}/tarball/master | /usr/bin/tar xz -m –strip 1'"
end
end
end
warn "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin is not in your PATH." unless ENV["PATH"].split(":").include? "#{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/bin"
ohai "Installation successful!"
puts
# Use the shell's audible bell.
print "\a"
# Use an extra newline and bold to avoid this being missed.
ohai "Homebrew has enabled anonymous aggregate user behaviour analytics."
puts <<-EOS
#{Tty.bold}Read the analytics documentation (and how to opt-out) here:
#{Tty.underline}https://docs.brew.sh/Analytics.html#{Tty.reset}
EOS
if git
Dir.chdir HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY do
system git, "config", "–local", "–replace-all", "homebrew.analyticsmessage", "true"
end
end
ohai "Next steps:"
if macos_version “10.6”
`/usr/bin/cc –version 2> /dev/null` =~ /clang-(\d{2,})/
version = $1.to_i
if version < 425
puts "- Install the #{Tty.bold}Command Line Tools for Xcode:"
puts " #{Tty.underline}https://developer.apple.com/downloads#{Tty.reset}"
end
elsif !File.exist? "/usr/bin/cc"
puts "- Install #{Tty.bold}Xcode:"
puts " #{Tty.underline}https://developer.apple.com/xcode#{Tty.reset}"
end
unless git
puts "- Run `brew update –force` to complete installation by installing:"
puts " #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/doc/homebrew"
puts " #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/man/man1/brew.1"
puts " #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/share/zsh/site-functions/_brew"
puts " #{HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/etc/bash_completion.d/brew"
puts " #{HOMEBREW_REPOSITORY}/.git"
end
puts "- Run `brew help` to get started"
puts "- Further documentation: "
puts " #{Tty.underline}https://docs.brew.sh#{Tty.reset}"
pc85:~ felicite$
pc85:~ felicite$
La commande curl va uniquement t’afficher le script. Il faut utiliser la commande complète selon l’article:
ruby -e “$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)”