There are two quick ways to configure an IP address on the network interface of the CentOS 8 operating system. The one is using nmtui command and another is by directly edition networking files.
If you are not comfortable to edit configuration files, choose option 1 to set up networking in an interactive way.
Method 1 – Using nmtui Tool
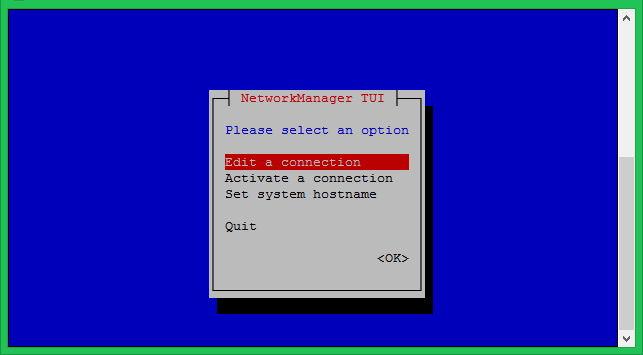
Execute the following command to get access to an interactive way of network interface configuration.
sudo nmtui
Now, edit the default existing connection. In case no connection is available, use Activate a connection.
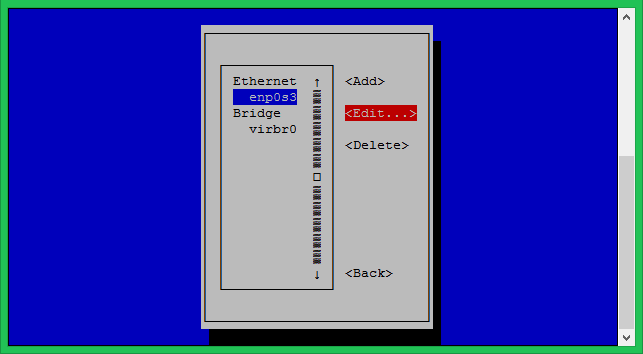
You will see the list of Ethernet interfaces, Select the interface you want to configure, Then select Edit option on the right side of the interface.
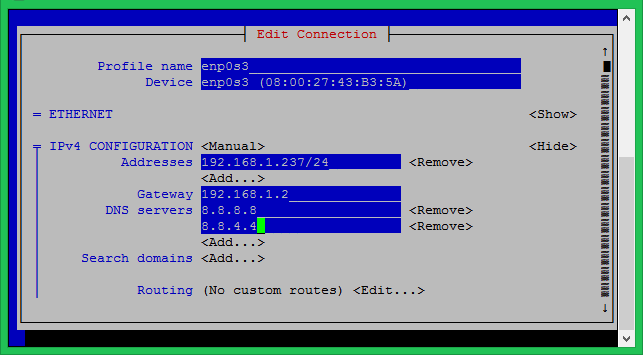
Keep the profile name and device name unchanged. Set the IP address, gateway and DNS servers under the IPv4 configuration option. You can add multiple addresses by selection
Save the configuration and restart the NetworkManager service using the following command.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
Method 2 – Using Configuration Files
The default netework interfaces configuration file exists in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. The file name may vary as per your installation type like Physical machine or Virtual machine. The configuration file shoul be like ifcfg-XXXX (eg: ifcfg-eth0, ifcfg-eth1, ifcfg-enp0s3 etc)
sudo vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
Use the following configuration to configure a static IP address for your CentOS 8 network interface.
Static IP Configuration:
TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=static NAME=enp0s3 DEVICE=enp0s3 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.1.237 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.1.2 DNS1=8.8.8.8 DNS2=192.168.1.2 USRCTL=no
Alternatively, if you want to assign IP address via the DHCP server use the following settings.
DHCP Configuration
TYPE = Ethernet DEVICE = enp0s3 BOOTPROTO = dhcp ONBOOT = yes
Details of configuration parameters:
- DEVICE: Ethernet device name
- BOOTPROTO: dhcp or static
- ONBOOT: yes/no , it tells that interface will automatically up or not on boot.
- Type: Type of interface.
- USRCTL: yes/no , it tells that a non root user can bring this device up or down.
Save the configuration and restart the NetworkManager service using the following command.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
All done.


1 Comment
Dear Rahul – I have a cluster with 4 ethernet connections for every node, including the master. But only 2 are used in the master (external and internal eth cables). After setting up the network, everything works fine. But I had to poweroff the cluster for some reason. After turning it on again, everything got waywire: the external eth did not work and neither could the internal connections to the nodes. After every reboot, the up/down status of the connections change. Is there a method to guarantee that connections will endure a reboot or a poweroff?