In Python, there are a few ways to accept user input. In this blog post, we will explore three different ways to do so. We will start with the simplest way and work our way up to the more complex methods. By the end of this post, you should have a good understanding of how to accept user input in Python. Let’s get started!
Python 3 provides a built-in function called input() that allows you to take user input. Where Python 2.x uses the raw_input() function is used to accept user input. Python 2.7 also has a function called input(). However, this function takes only one argument: the prompt string.
Lets see a few examples:
- Python 3.x – Using input() function123name = input("Enter your name: ")print("Hello", name)
Open a Python shell and run the above statements.

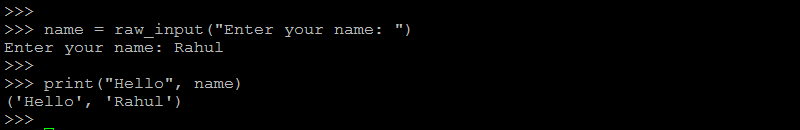
Python3 read() function - Python 2.x – Using raw_input() function123name = raw_input("Enter your name: ")print("Hello", name)
This is similar to the input() function of Python 3.
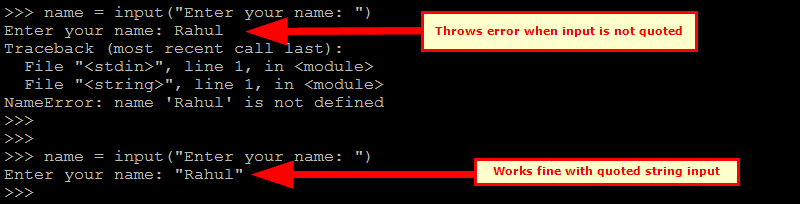
Python 2.7 raw_input() function - Python 2.x – Using input() function 123name = input("Enter your name: ")print("Hello",name)
Run the above scripts in the Python shell and input a string without any quotes. Python will return an error message. Now again run the same script and input a string with quotes. This will work.
Python 2.7 input() function
