Kubernetes is a powerful and widely adopted container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. In this comprehensive introduction, we will cover the basics of Kubernetes for beginners, including its history, architecture, key components, and benefits. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of the platform and be well on your way to leveraging Kubernetes for your own container-based projects. Table of Contents The Emergence of Containers and Kubernetes Kubernetes Architecture Nodes Control Plane etcd Key Components of Kubernetes Pods Services Deployments ConfigMaps and Secrets Ingress Benefits of Kubernetes Getting…
Author: Rahul
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security measure that’s designed to provide an additional layer of protection for your online accounts. In this tutorial, we’ll dive deep into what 2FA is, how it works, and how you can set it up for your accounts. What is Two-Factor Authentication? Two-factor authentication is a security procedure that requires users to provide two distinct forms of identification before they can access their accounts. Typically, this involves something the user knows (like a password) and something the user has (like a mobile device). The goal of 2FA is to provide an extra layer of security.…
Squid is a versatile tool that serves as both a proxy server and a web cache system. It helps speed up web browsing by storing frequently accessed content and can also block certain websites. In this guide, we’ll show you how to use Squid to block specific websites. Sometimes we need to to block some specific websites to keep our network safe, save on bandwidth, increase productivity by reducing distractions, or follow company rules and regulations. You can do this by installing a proxy server between the internet and computers. Which will act a middle man to filter traffic and…
In the realm of software development, version control is paramount. Among the various version control systems available, Git has emerged as an industry standard due to its robustness, flexibility, and distributed architecture. In this article, we’ll be focusing on the fundamental steps of a basic Git workflow: Add, Commit, and Push. Understanding Git Before delving into the intricacies of Git’s workflow, it’s crucial to understand what Git is. Git is a distributed version control system that allows multiple developers to work on a project simultaneously without overwriting each other’s changes. This is achieved by creating different versions of the project,…
In the continually evolving world of cybersecurity, understanding various types of threats is the first step in protecting yourself or your business. One such common yet significant threat is a brute-force attack. Let’s delve into understanding what a brute-force attack is, how it works, and its implications. What is Brute-Force Attack A brute-force attack is a trial-and-error method used to obtain information such as personal identification numbers (PINs), user names, passwords, or other types of security keys. The fundamental idea behind a brute-force attack is exceedingly simple: try all possible combinations until the correct one is found. As the name…
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is a common cyber-security threat that can have severe consequences if not properly addressed. In this type of attack, a malicious actor intercepts, relays, and potentially alters the communication between two parties who believe they are communicating directly with each other. This article will delve into the threats posed by MITM attacks, the techniques used by attackers, and the countermeasures that individuals and organizations can use to protect themselves. Threats Posed by MITM Attacks The most apparent threat posed by MITM attacks is the unauthorized access to sensitive information. By intercepting the communication between two parties,…
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is a protocol used in computer networking, with the primary role of translating physical network addresses (MAC addresses) into IP addresses. RARP is the inverse of the more widely recognized Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which, conversely, translates IP addresses into MAC addresses. Understanding RARP: The Basics RARP operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model. RARP’s primary application was to support diskless workstations. These machines do not have a hard disk to store their IP addresses. Therefore, when they start up, they require a mechanism to discover their…
Git is a widely-used version control system that allows developers to manage and track the changes made to files in a project. Understanding Git’s terminologies and concepts, including untracked files, is key to effectively using Git for version control. This article will explore what untracked files are in Git, why they exist, and how to manage them. To ensure a comprehensive understanding, we’ll provide examples for each concept discussed. Understanding Untracked Files in Git In the Git version control system, an untracked file is simply a file that is not monitored by Git. When you create a new file in…
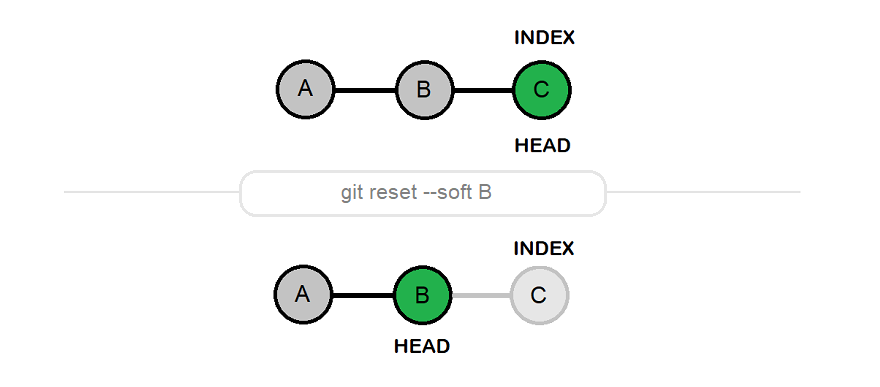
Git is one of the most popular Version Control Systems (VCS) currently in use, and it provides a wide range of commands to manage and manipulate the history of your codebase. Understanding these commands and their subtleties can significantly improve your efficiency and the way you work with a codebase. One such command is git reset, which comes with a few options that can significantly change its behavior: –soft, –mixed, and –hard. Introduction to Git Reset The git reset command is a powerful tool used to undo changes in a Git repository. It essentially allows you to move the HEAD…
Git, the popular distributed version control system, introduces a unique feature in its workflow known as the “staging area” or “index”. This intermediate space acts as a preparatory area for commits, providing developers with fine-grained control over their version history. To leverage Git to its full potential, it’s essential to grasp the concept and purpose of the staging area. 1. The Three-Tiered Architecture of Git Before delving into the specifics of the staging area, it’s crucial to understand the three-tiered architecture of Git: the Working Directory, the Staging Area, and the Git Repository. Working Directory: The working directory is where…