As a system administrator, you deals regularly with multiple remote systems. You need to SSH systems multiple times during your work. Many of remote Linux server you have access through password a many of them you have access through private key. So this can be more typical to manage all of them.
This article will help you to properly organize your ssh server details with key files.
Configuration File Syntax:
We can add multiple ssh hosts details to ~/.ssh/config file. Edit configuration file in your favorite editor like vi, vim or nano.
$ vi~/.ssh/config
The syntax will be like below.
Host <NICK_NAME>
HostName <IP ADDRESS OF REMOTE>
IdentityFile <PATH TO PRIVATE FILE>
User <LOGIN AS USERNAME>
Port <SSH PORT TO USE>
LocalForward <LOCAL PORT> <REMOTE_LOCATION:PORT>
1. Add First SSH Host
For example we have our first SSH host is running a PHP development web server with details nick name as php-web1, user root, port 22 and accessible through password. Add the following content in configuration file.
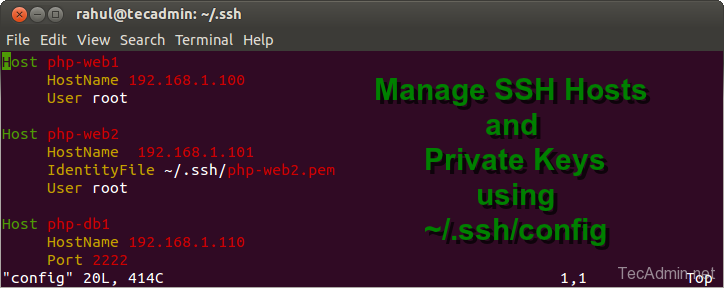
Host php-web1
HostName 192.168.1.100
User root
Now try SSH as following command.
$ ssh php-web1
2. Add Second SSH Host
Our second host server (php-web2) is accessible with ssh key-pair with user root on default port 22. Add the following content in configuration file.
Host php-web2
HostName 192.168.1.101
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-web2.pem
User root
Now try SSH as following command.
$ ssh php-web2
3. Add Third SSH Host
Our third ssh host server (php-db1) is running on port 2222, accessible though key-pair with user ubuntu. Add the following content in configuration file.
Host php-db1
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
User ubuntu
Now try SSH as following command.
$ ssh php-db1
4. Setup Forwarding with SSH
In this setup we need to forward our local system port 3306 to remote servers (php-db1) hosts on port 3306 . Add the following content in configuration file.
Host php-db1-mysql-tunnel
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
LocalForward 3306 127.0.0.1:3306
Now try SSH as following command.
$ ssh php-db1-mysql-tunnel
Final Configuration File
Your final configuration file ~/.ssh/config will look like below.
Host php-web1
HostName 192.168.1.100
User root
Host php-web2
HostName 192.168.1.101
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-web2.pem
User root
Host php-db1
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
User ubuntu
Host php-db1-mysql-tunnel
HostName 192.168.1.110
Port 2222
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/php-db1.pem
LocalForward 3306 127.0.0.1:3306