Time zones play a crucial role in ensuring that the system clock displays the correct time, particularly in a multi-user environment. Keeping the system time in sync with the right time zone helps to avoid confusion, reduce errors, and enhance the reliability of your systems.
In this article, we will cover the steps involved in configuring the time zone in CentOS Steam 9/8 and other RHEL-based systems, which is a popular Linux distribution used in enterprise environments.
Before we get started, it is important to note that you will need root access to your system to perform the steps outlined in this guide.
Step 1: View the Current Time Zone
Before making any changes to the time zone, it’s always a good idea to check the current time zone of your system. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
timedatectl
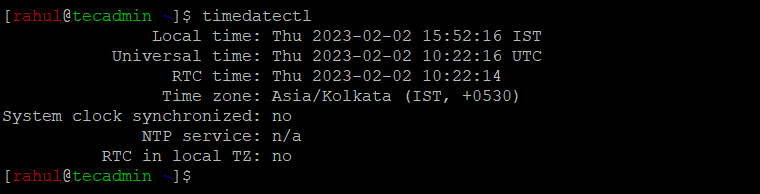
The above output showing that the current timezone is set to “Asia/Kolkata” alsoing with the current system time, date, and time zone information.
Step 2: List Available Time Zones
The CentOS Steam 9/8 and other RHEL-based system supports a large number of time zones, and you can view a list of all available time zones by running the following command:
timedatectl list-timezones
This command will display a list of all the supported time zones, which you can use to determine the correct time zone for your system.
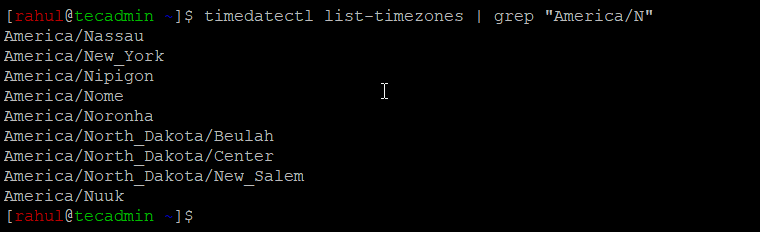
timedatectl list-timezones | grep "America/N"
In the above output, you will get a long list of available packages. You can also filter the output with grep command.
Step 3: Change the Time Zone
To change the time zone in RHEL/CentOS Steam 9/8, you can use the `timedatectl set-timezone` command. For example, to change the time zone to “America/New_York”, you would run the following command:
timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York
Its always recommended to use the universal timezone (UTC) for the servers and then manager your applications accordingly. This way its easier to handle application between cross regions and timezones.
timedatectl set-timezone "UTC"
The above commands replaces the link for the /etc/localtime file and set them to requested timezone file available udner /usr/share/zoneinfo directory. Which you can also do manaully, instead of using the above commands. For example, to change timezone to the “America/New_York” time zone, you would run the following command:
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/New_York /etc/localtime
After running this command, the time zone change will persist across reboots.
Step 4: Verify the Change
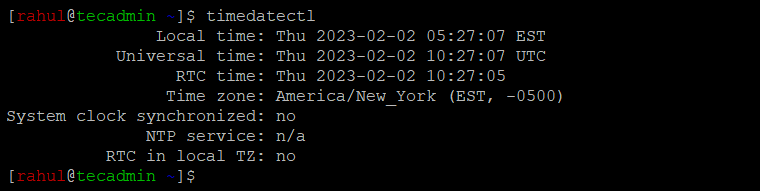
After changing the time zone, you can verify the change by running the timedatectl command again. The output should display the updated time zone information.
timedatectl
You should see the updated timezone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, configuring the time zone in CentOS Steam 9/8 other RHEL-based systems is a straightforward process that can be performed by following these simple steps. Keeping the system time in sync with the correct time zone helps to enhance the reliability of your systems and avoid confusion.



5 Comments
Wonderful. I have been looking for this. Too many variations of Linux. Hard to find the commands sometimes.
Thanks for sharing
Site added to my list 🙂
Dude!!! You are man! Full of balls !
Hi i have two question
1. i want to update my server time without NTP
2. i want to delete specifics files from the server
for eg :- in my system files from 1 march 2017, i want to delete files only specific period of time,means
i want my files from date 04.06.2017 till today.but won’t delets files that is store or are older than
03.06.2017.
Yes, this worked. Many thanks!
Thank You, Sir!
To check if you have RHEL 6 or 7 to use the awesome timedatectl command you can execute uname – r.
Else the primitive way is also ok with more than a single step.