DNS caching is a technique used by operating systems and applications to temporarily store DNS query results, reducing latency and improving overall internet browsing performance. However, there may be times when you need to clear the DNS cache, especially when cached records are outdated or causing connectivity issues. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to flush the DNS cache in Windows.
Windows operating systems maintain a local DNS cache to speed up the resolution of domain names to IP addresses. When you visit a website, the operating system first checks the local DNS cache for the corresponding IP address. If the record is not found, a DNS query is sent to the configured DNS server. The response is then cached locally to speed up future queries for the same domain name.
Flushing DNS Cache in Windows
To flush the DNS cache in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type cmd in the Run dialog box and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
- In the Command Prompt, type the following command and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdnsIf the command is executed successfully, you should see a message stating, “Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache”.
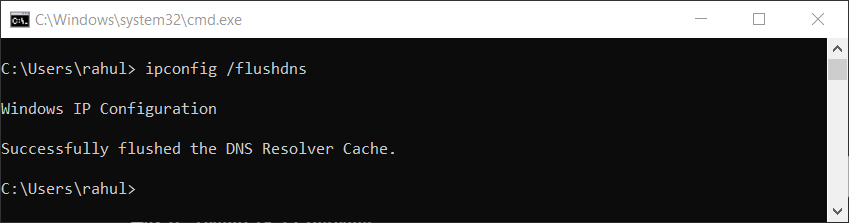
Clearing DNS Cache in Windows
Clearing DNS Cache in Web Browsers
Web browsers like Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox also maintain their DNS caches to speed up web browsing. To clear the DNS cache in your browser, follow the instructions specific to your browser:
- Google Chrome: Navigate to “chrome://net-internals/#dns” and click the “Clear host cache” button.
- Mozilla Firefox: Type “about:networking#dns” in the address bar, then click the “Clear DNS Cache” button.
Conclusion
In this article, we provided a step-by-step guide on how to flush the DNS cache in various versions of the Windows operating system, including Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows XP. Additionally, we discussed how to clear the DNS cache in popular web browsers. Clearing the DNS cache can help resolve connectivity issues caused by outdated or incorrect DNS records, ensuring a smoother browsing experience.
