In the vast expanse of the digital universe, every website visit begins with an unseen but crucial process, as integral to your online journey as a compass is to navigation. This process is powered by the Domain Name System (DNS), a foundational technology of the internet. Understanding how DNS works is like unveiling the wizard behind the curtain of the online world. This article demystifies the Domain Name System, explaining its function, how it works, and why it’s essential for your browser to find websites.
What is the Domain Name System (DNS)?
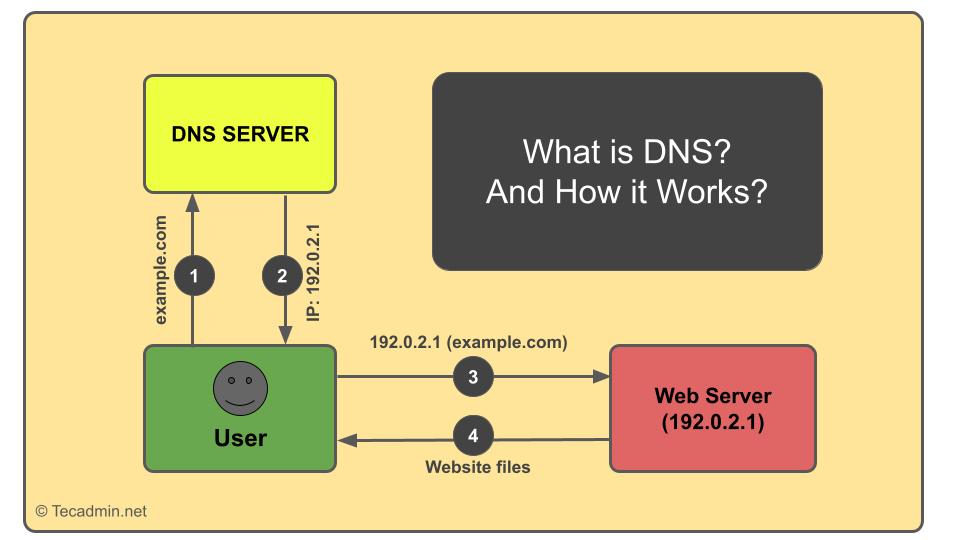
The Domain Name System is often likened to the internet’s phonebook. In the days before digital contact lists, if you wanted to call someone, you’d look up their name in a phone book to find their telephone number. Similarly, DNS translates human-friendly domain names, such as “example.com”, into machine-readable IP addresses, like “192.0.2.1”, that computers use to connect with each other.
DNS is a decentralized system, ensuring no single point of failure can disrupt the entire internet. It consists of a worldwide network of servers working in concert to provide the necessary translations that enable browsers to load internet resources.
How Does DNS Work?
When you type a website’s domain name into your browser, the DNS process kicks off with a series of queries to find the corresponding IP address:
- DNS Resolver Query: Your browser first sends a query to a DNS resolver, typically operated by your internet service provider (ISP). The resolver acts as your first point of contact in the quest to find the website’s IP address.
- Root Nameserver Query: The resolver then reaches out to a root nameserver. Root nameservers are at the top of the DNS hierarchy and can guide the resolver to specific servers that know more about the domain in question.
- Top-Level Domain (TLD) Nameserver Query: Next, the query is directed to a TLD nameserver (e.g., for “.com” or “.net” domains). This server knows the whereabouts of the servers responsible for the domain’s next level.
- Authoritative Nameserver Query: Finally, the resolver reaches the authoritative nameserver for the specific domain. This server has the actual IP address for the domain name and sends it back to the DNS resolver.
- Resolution and Connection: With the IP address now known, the DNS resolver sends it to your browser, which can then request the webpage from the web server associated with that IP address.
This entire process, fascinatingly, takes only milliseconds to complete.
Why is DNS Important?
DNS is crucial for several reasons, including:
- Usability: DNS makes the internet accessible and user-friendly. Remembering numerical IP addresses for all the websites we visit would be impractical. DNS allows us to use easy-to-remember names instead.
- Scalability: The decentralized nature of DNS, with its distributed network of servers, ensures the system can handle billions of requests efficiently and reliably.
- Flexibility: DNS allows domain names to be easily moved between IP addresses, facilitating changes in hosting and internet infrastructure without affecting the end user’s experience.
Security and Privacy in DNS
While DNS is a robust system, it’s not without its vulnerabilities. Security threats like DNS spoofing can redirect users to malicious websites. To combat these risks, DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) provides a layer of security that verifies DNS responses are authentic.
Privacy concerns also arise with DNS queries potentially being intercepted or logged. Solutions like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) encrypt DNS queries, preventing eavesdropping and enhancing user privacy.
Wrap Up
The Domain Name System is a silent guardian of the internet, a critical infrastructure that makes browsing the web as seamless as turning the pages of a book. By translating domain names into IP addresses, DNS ensures that the vast digital landscape remains navigable and accessible. Understanding the workings of DNS not only demystifies a key aspect of internet technology but also underscores the importance of security and privacy in the digital age. As we continue to explore and expand the internet, the role of DNS will only grow in significance, ensuring that our journey through the digital world remains smooth and secure.