Managing updates on your Ubuntu system is important to keep everything running smoothly. Sometimes, you might want to keep certain software packages at their current versions and not let them update. This is called excluding packages from upgrades.
In this guide, we will show you how to stop specific packages from being updated using the apt-get upgrade command. Even if you are new to Ubuntu or computers in general, don’t worry! We will explain everything in easy steps so you can follow along. By the end, you’ll know how to keep certain packages from updating, which can help keep your system stable and working just the way you like it.
Commands to Exclude Packages from Upgrade
To stop specific Debian packages from updating, use these commands. This will prevent the chosen packages from being automatically or manually updated.
- Using apt
sudo apt-mark hold package_name - Using dpkg
echo "package_name hold" | sudo dpkg --set-selections - Using aptitude
sudo aptitude hold package_name
Replace package_name with the actual name of the package you want to hold.
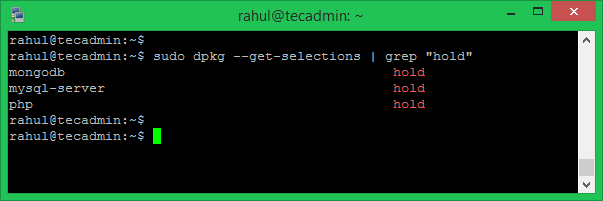
List All Packages on Hold
You can check which packages are on hold at any time. Use this command to see all the packages that are set to hold.
sudo dpkg --get-selections | grep "hold"
Re-enable (Unhold) Package Upgrade
If you need to update a package that is on hold, you must unhold it first. Use one of these commands to unhold a package.
- Using apt
sudo apt-mark unhold package_name - Using dpkg
echo "package_name install" | sudo dpkg --set-selections - Using aptitude
sudo aptitude unhold package_name
Now, the unheld packages will be updated with `apt upgrade` or unattended upgrades.
Conclusion
By using these commands, you can easily control which packages get updated on your Ubuntu system. This helps keep your system stable by preventing updates to certain packages. Whether you use `apt`, `dpkg`, or `aptitude`, managing package upgrades becomes simple. Remember, you can always check which packages are on hold and unhold them if needed. This way, you have full control over your system’s updates.

4 Comments
Hi Rahul,
In my experience, in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, with kernel 4.15.0-120, if you want to ‘hold’ the kernel it in that version, but if you still have installed the packages:
linux-image-generic
linux-headers-generic
linux-image-generic-hwe-16.04
linux-headers-generic-hwe-16.04
It will NOT work. Took me a while to figure it out, since apt-mark, aptitude hold, and dpkg –set-selections methods were not preventing the install of new version of the Linux kernel.
Basically, remove these packages. They do not provide the kernel, so you won’t break the system.
They are a placeholder for all kernel packages versions, so the apt system knows that it has to install (instead of update the package as it would be with all other packages — kernel is a special package in this concern!) a new package in order for the kernel to be updated.
This worked for me:
apt remove linux-image-generic linux-headers-generic linux-image-generic-hwe-16.04 linux-headers-generic-hwe-16.04
I hope this helps someone else 🙂
In the section: “Unhold or Include Package in Install”, the unhold command for aptitude is slightly wrong. Should be unhold not hold 🙂
Thanks Jack, I have corrected the command.
Thanks for the post!