Disk space is used to refer to the computer space amount on the hard drive, floppy, USB, etc, and is usually measured in large units like kilobytes, megabytes. We can also simply say that disk space is the maximum amount of data that a disk is capable of holding and any type of media that can hold some data have disk capacity.
As we save data to a disk, the disk usage increases day by day and it is important to monitor that data so our disk capacity or disk space doesn’t reach its limit. We can monitor data on any device including computers, mobiles, laptops as well as Linux servers. Suppose you have a 200GB hard disk and you are going to install PubG game on your computer which requires at least 30GB of free space on your hard drive. In this case, first, you are going to check the disk space and make sure that 30GB is available to download and install the pubg game.
In this article, all the necessary steps will be taken to teach you how to check disk space in Ubuntu 20.04 with two methods which are graphical user interface (GUI) and also via command line/ terminal.
Checking Disk Space via GUI
Click on the show applications which is present at the left bottom corner of the viewscreen of your Ubuntu system:
When you click on the show Applications you will see a search bar at the top:
Disks GNOME is by default installed in Ubuntu 20.04 as well as 20.10 and you don’t need to manually install Disks GNOME. Search for disks in the search bar shown in the above screenshot. When you are done you will see an application with the name of Disks, click on it:
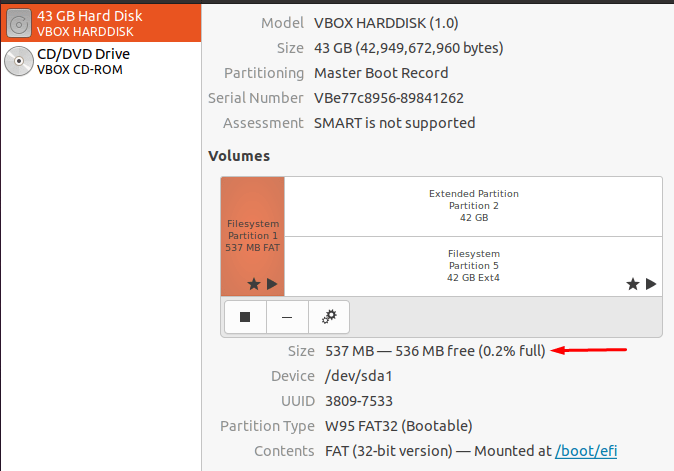
When you select or click on the Disks GNOME you will be directed towards the Disks utility where you will see total disk size as well as disk space:
Check Disk Space via Ubuntu Terminal
To check disk space via Ubuntu terminal, we will use the following two commands:
1) df command [what is this ??]
The full form of df is Disk Filesystem and this is by default installed in Ubuntu 20.04 whose function is to show various file systems information and can be executed like shown below:
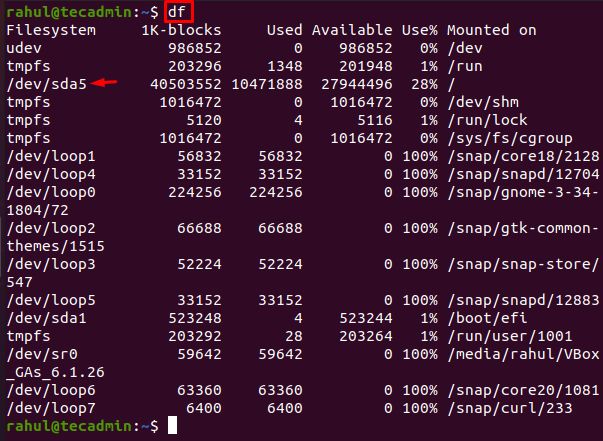
df
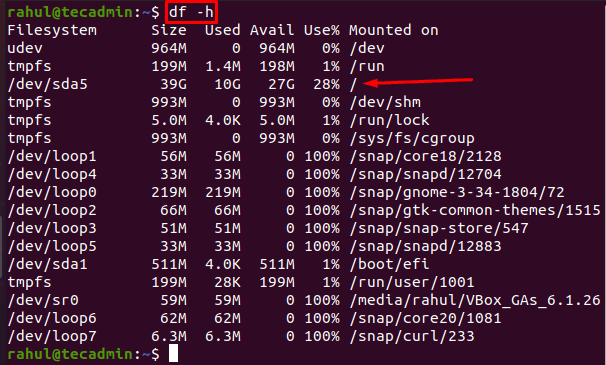
When we executed the df command we were shown all the available space as well as the total used space (in numbers and percentage). The /dev/sda5 is the system’s actual disk and the command df showed information in 1k-blocks which is difficult to interpret.
The solution is to use the -h option with the df command which will display information in a human-readable form:
df -h
We can see in the above screenshot that the disk space is in gigabytes, the total disk size is 29 gigabytes, 13 and 15 gigabytes is the used and available space and the file system is /dev/sda.
2) du command
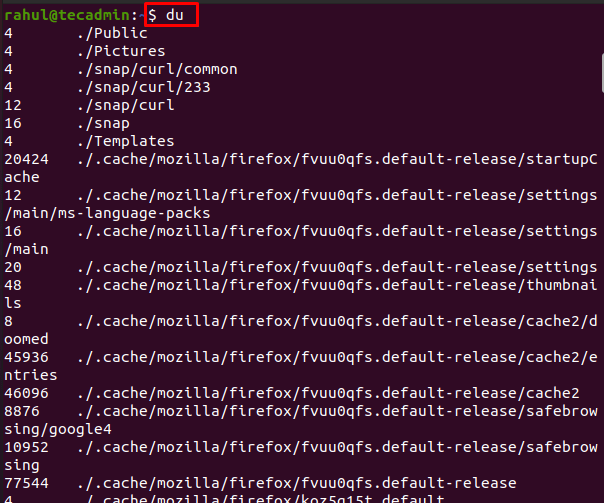
Du full form is Disk Usage and the purpose of this command is to show the users all the information about every directory as well as the subdirectory and can be executed as follows:
du
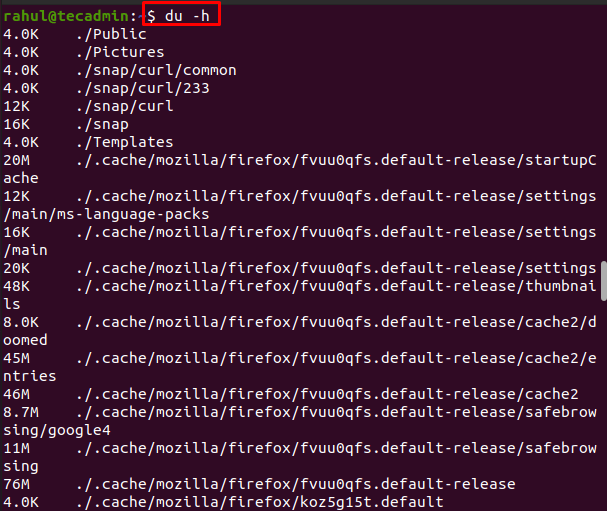
In the above screenshot, we can see that all the directories and the subdirectories sizes are displayed in the 1K block. The -h command used with the df command can also be used with the du command and the function of the -h option is the same as it helps users in displaying data in human-readable form:
In the output, it can be seen that the disk usage is displayed in kilobytes and megabytes.
Conclusion
The maximum amount of data that a disk can hold is its disk space and monitoring disk space is a necessity as the data saved on our disks is increasing day by day. By checking disk space we will know what applications or files are taking a lot of space and hence we can uninstall or delete them to free up space which will give us smooth system usage.
In this article, all the necessary steps were shown to you on how to check disk space in Ubuntu 20.04 via GUI as well as command-line interface/terminal. In the command-line interface, we discussed the du and df commands to check disk space. We hope that now you can monitor your data on Ubuntu with these techniques.