SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides enhanced security for Linux systems. SELinux provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies. This specifies how the processes communicate with each other and interact with the files.
We never recommend disabling SELinux on your system, especially on production servers. For developer systems, you can disable it only if hampering your work due to its policies.
SELinux Modes:
SELinux has three modes to run as described below. The default SELinux runs in Enforcing mode on a Fedora Linux system.
- Enforcing – SELinux security policy is enforced.
- Permissive – SELinux allows access but prints warnings on rules violations.
- Disabled – No SELinux policy is loaded.
In this article, we will discuss how to change SELinux mode to permissive or disable it completely on a Fedora Linux system.
Check SELinux Status
You can use getenforce command to view the status of SELinux. Another command sestatus gives you more details about SELinux status.
Open a terminal on your Fedora systems and type:
sestatus
You will see the ouptut as:
SELinux status: enabled SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux Loaded policy name: targeted Current mode: enforcing Mode from config file: enforcing Policy MLS status: enabled Policy deny_unknown status: allowed Memory protection checking: actual (secure) Max kernel policy version: 33
The above status shows that SELinux is enabled and enforced.
Set SELinux in Permissive Mode (Temporary)
The permissive mode means the SELinux policy is not enforced. SELinux does not deny any operations even if they do policy violations. It only creates logs, which is helpful for debugging.
You can set the SELinux in permissive mode temporarily by using one of the below commands.
sudo setenforce 0
sudo setenforce Permissive
Once the system is rebooted, the temporary mode will be disabled and SELinux will again in enforcing. Use the next method to apply changes permanently.
Set SELinux in Permissive Mode (Permanent)
You can also Configure SELinux Permissive Mode Permanently by editing the configuration file. Edit the configuration in in your favorite text edit:
sudo nano /etc/selinux/config
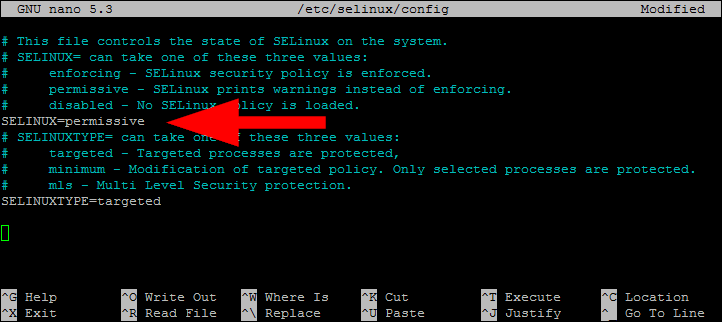
Set the SELINUX value to permissive.
SELINUX=permissive
File changes will reflect after the system reboot.
Permanently Disable SELinux on Fedora
Update the SELinux configuration file and set SELINUX=disabled to permanently disable the SELinux on your system. This will completely disable all the SELinux contexts.
sudo nano /etc/selinux/config
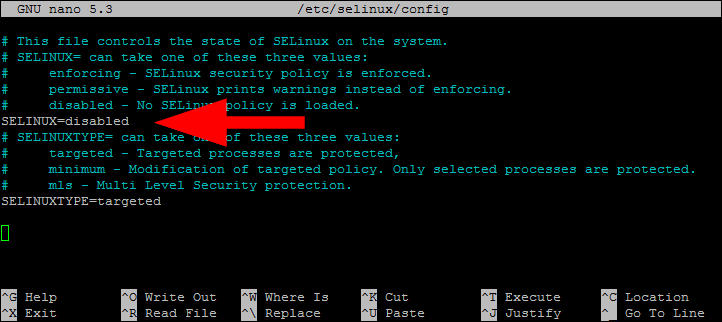
Set SELINUX value to disabled:
SELINUX=disabled
Reboot your instance after making changes.
Note – You can again activate the SELinux by setting SELINUX=enforcing in configuration file.
Concusion
In this tutorial, you have learned about configuring SELinux in permissive mode or disabling it completely on a Fedora Linux system. This tutorial can be followed on other Redhat-based distributions like CentOS, RHEL, etc.