Gitlab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle management tool developed by GitLab Inc. It provides git version control repository management, issue tracking, a To-Do list, continuous integration, and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines for the applications. Gitlab also supports integration with various services.
The Community edition of Gitlab is available free for use in the development and production environment. It provides a large number of features required for small to large-scale companies. The enterprise edition provides more features but required a paid license.
This tutorial will help you to install Gitlab on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Linux system. You are going to install Gitlab community edition using this tutorial.
Prerequisites
Login to your Ubuntu 20.04 system with sudo privileged account.
Then upgrade the current packages to the latest version.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Also, install some required packages for installing Gitlab on Ubuntu systems.
sudo apt install -y vim curl ca-certificates apt-transport-https
Step 1 – Install Gitlab on Ubuntu 20.04
The Gitlab official team provides a shell script to configure Apt repository on your system. As well as install some required dependencies to your system.
Open a terminal and execute following command:
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
The above command will create apt configuration file (/etc/apt/sources.list.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.list) in your system. Next is to install Gitlab on Ubuntu system using apt command:
sudo apt install gitlab-ce
This command will take some time to complete the Gitlab installation on Ubuntu. This will install all the required services like Nginx, PostgreSQL, Redis, etc.
Step 2 – Configuring Gitlab
Edit the Gitlab configuration file /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb and update the external url to a valid domain or subdomain name to use for accessing Gitlab.
sudo vim /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
external_url "https://gitlab.tecadmin.net"
The Gitlab also provides native support for configuring let’s encrypt SSL certificates. To enable the let’s encrypt SSL, edit the following values in the configuration file.
# Enable the Let's encrypt SSL letsencrypt['enable'] = true # This is optional to get SSL related alerts letsencrypt['contact_emails'] = ['[email protected]'] # This example renews every 7th day at 12:30 letsencrypt['auto_renew_hour'] = "12" letsencrypt['auto_renew_minute'] = "30" letsencrypt['auto_renew_day_of_month'] = "*/7"
Save the configuration file. The vim editor user use ESC + :wq to save and exit file. The nano user can use shotcut CTRL + o to save content and then CTRL + x to exit from editor.
Now, run the reconfigure command to apply changes to the Gitlab server.
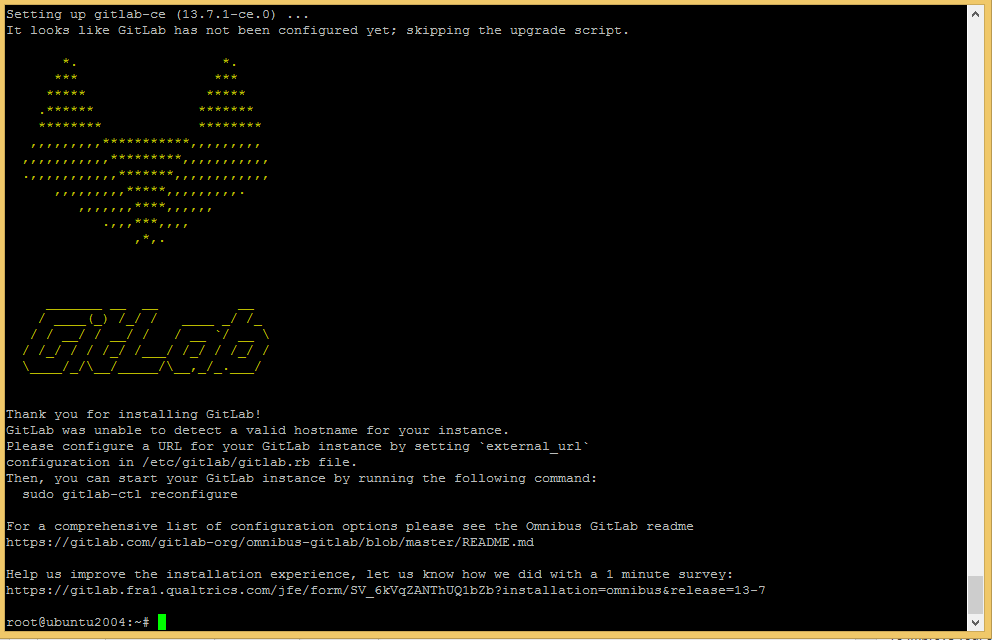
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
This will take some time to complete the installation. In the end, you will see the message “gitlab Reconfigured!” on your screen.
Step 3 – Adjust Firewall
If your system running a firewall, make sure to open 80, 443 ports.
The firewalld users can use the following commands to open required ports on their system.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=httpsudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
Next, run the following command to implement the changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4 – Access Gitlab Dashboard
Access the Gitlab dashboard using the domain name configured in the Gitlab configuration file. Open a web browser and access your domain:
https://gitlab.tecadmin.net
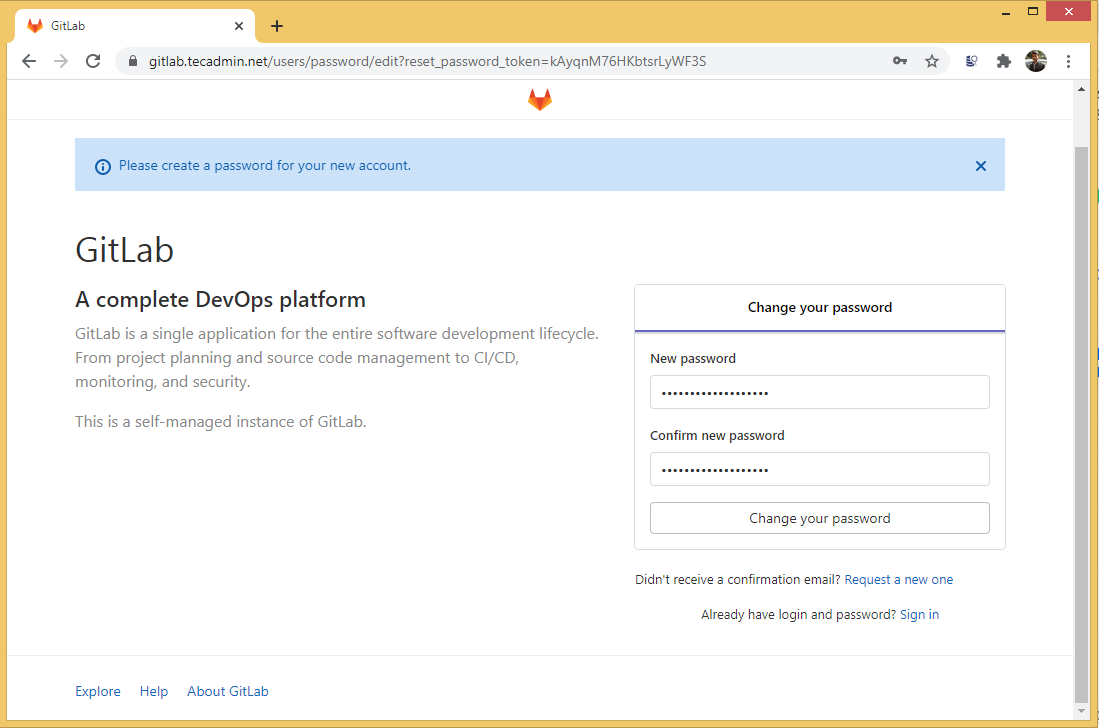
During the first time, Gitlab will prompt you to set a new password for the default user. The Gitlab default username is “root”, have the administrator privileges. Set a strong password for this account.
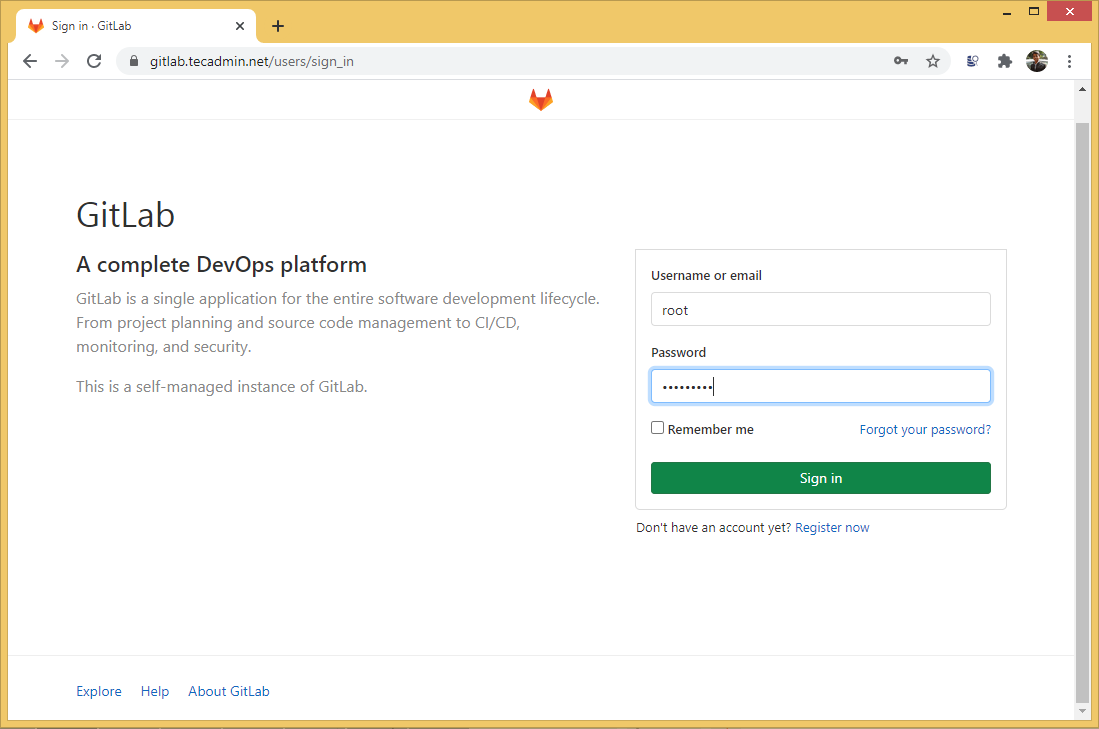
After changing the password, your browser redirects to the login page. Here use “root” as the username and password, you set in above to log in as an administrator.
Hit Sign in button to login Gitlab administrator dashboard.
You have successfully installed Gitlab on your Ubuntu system. Next, create users, groups, and repositories for your code to be managed under the Git version control system.
Step 5 – Configure Backups
Use the following command to take a complete backup of your data. The default backup created under the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory, which can be change in /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb file.
sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:backup:create
You can also add the same command scheduler to back up data nightly. Add the below job to the system crontab.
0 22 * * * sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:backup:create
Conclusion
This tutorial helped you to install and configure Gitlab on the Ubuntu system. Also provides you instructions to configure let’s encrypt SSL on Gitlab.