In this guide, we will learn how to install phpMyAdmin on your macOS. We will use Homebrew to install Apache (the web server) and PHP, and then we will download phpMyAdmin manually from the official source. Let’s go step by step.
Step 1: Install Homebrew
Homebrew is a package manager for macOS that makes it easy to install software.
- Open Terminal on your Mac.
- Run this command to install Homebrew:
- After installation, run this to make sure Homebrew is set up correctly:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
brew --version
Step 2: Install Apache
Apache is the web server that will run phpMyAdmin.
- In your Terminal, type the following command to install Apache:
- Once it is installed, start Apache with this command:
- To check if Apache is running, open a web browser and go to
http://localhost. You should see a message that says “It works!”
brew install httpd
sudo brew services start httpd
Step 3: Install PHP
PHP is the programming language used by phpMyAdmin.
- Run the following command to install PHP:
- After PHP is installed, start it using:
- You can check the PHP version with this command:
brew install php
brew services start php
php -v
Step 4: Download phpMyAdmin
Now, we will download phpMyAdmin from the official website.
- Open the phpMyAdmin website in your browser: https://www.phpmyadmin.net/
- Click on the Download button and choose the latest version in the .zip format.
- Once downloaded, unzip the file and move the folder to your Apache server directory. By default, this directory is located at:
- You can move the unzipped phpMyAdmin folder with this command:
/usr/local/var/www/
sudo mv ~/Downloads/phpMyAdmin-*-all-languages /usr/local/var/www/phpmyadmin
Step 5: Configure Apache for phpMyAdmin
We need to tell Apache where phpMyAdmin is located.
- Open the Apache configuration file in a text editor:
- Look for the line that starts with:
- Remove the
#at the beginning of the line to enable PHP. - Scroll down and add this line to the file to include phpMyAdmin:
- Save the file and exit the editor (press
CTRL + X, thenY, and pressEnter). - Restart Apache to apply the changes:
sudo nano /usr/local/etc/httpd/httpd.conf
#LoadModule php_module
Alias /phpmyadmin "/usr/local/var/www/phpmyadmin"
sudo brew services restart httpd
Step 6: Access phpMyAdmin
You can now access phpMyAdmin in your web browser.
- Open your browser and go to this address:
- You should see the phpMyAdmin login screen. Use your MySQL username and password to log in.
http://localhost/phpmyadmin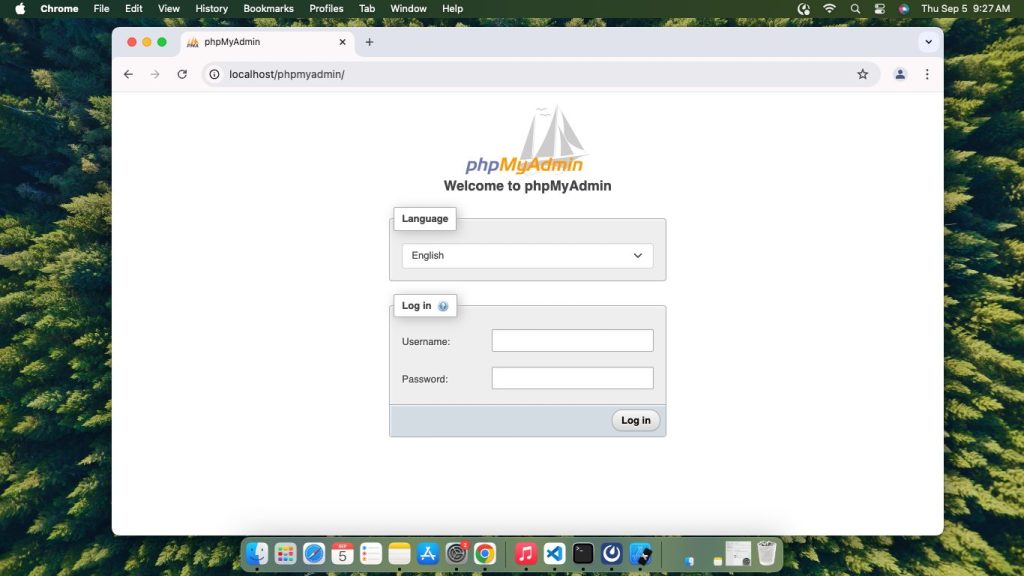
Step 7: Secure phpMyAdmin (Optional)
For security, it’s a good idea to restrict access to phpMyAdmin by adding a login prompt. To do this:
- Open the phpMyAdmin configuration file:
- Add this content to the file:
- Create a password file with this command:
- Restart Apache again:
sudo nano /usr/local/var/www/phpmyadmin/.htaccess
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Restricted Access"
AuthUserFile /usr/local/etc/httpd/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/etc/httpd/.htpasswd yourusername
sudo brew services restart httpd
Conclusion
You’ve successfully installed phpMyAdmin on your macOS using Apache and PHP! Now, you can manage your MySQL databases easily through phpMyAdmin. If you face any issues, make sure all services are running correctly and double-check the configuration files.


