Pip is a package installation tool that is used to get packages from the Python Package Index and various repositories.
Pip, which stands for “Preferred Installer Program”, is a Python-based package management application that streamlines the package installation and management process. Pip is a multi-platform package manager for Python projects which assists in managing libraries and dependencies. Pip installation on Ubuntu Linux is a quick and straightforward procedure.
The latest Python 3 is included in the standard system installation starting with Ubuntu 20.04. The source code for Python 2 may be found in the general source repository. However, users are encouraged to upgrade to Python 3. When there isn’t a corresponding package for a module, use pip to install it globally. Instead of installing Python modules globally, the Python virtual environment allows you to install them in a separate place beneath each project. You won’t have to worry about impacting other Python programs this way.
This article will show you how to set up Python 3 and Python 2. We’ll go through the basics of using pip to install and manage Python packages in Ubuntu 20.04.
How To Install PIP on Ubuntu 20.04
You can get the list of all compatible packages from the python packages official website (PyPI). You can also get help regarding installation using this website. For example, if you want to install any package like “scrapy” which is a package used for web scraping. Other than that, you can also get the documentation of the package for your better understanding.
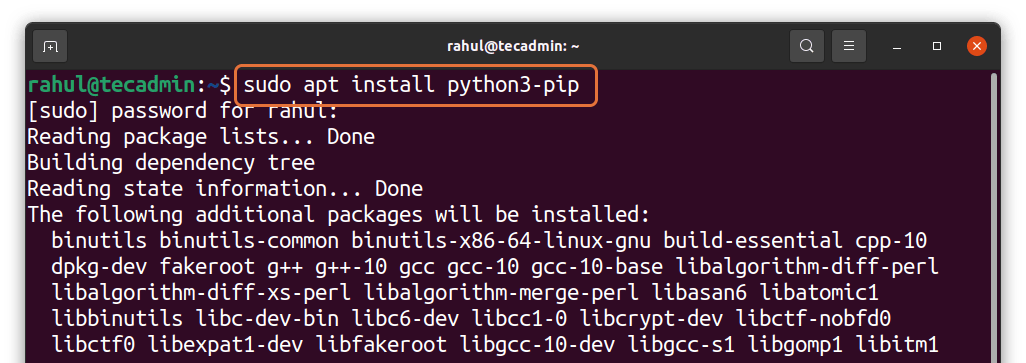
To install the pip file for python you need to type the command mentioned below:
sudo apt install python3-pip
It will prompt you and ask for your permission whether you want to install it or not (y/n), where you need to press “y” for installation as shown below.
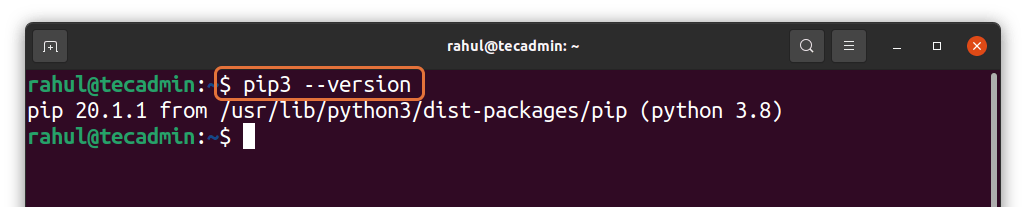
The installed version of pip can be identified using the command mentioned-below:
pip3 --version
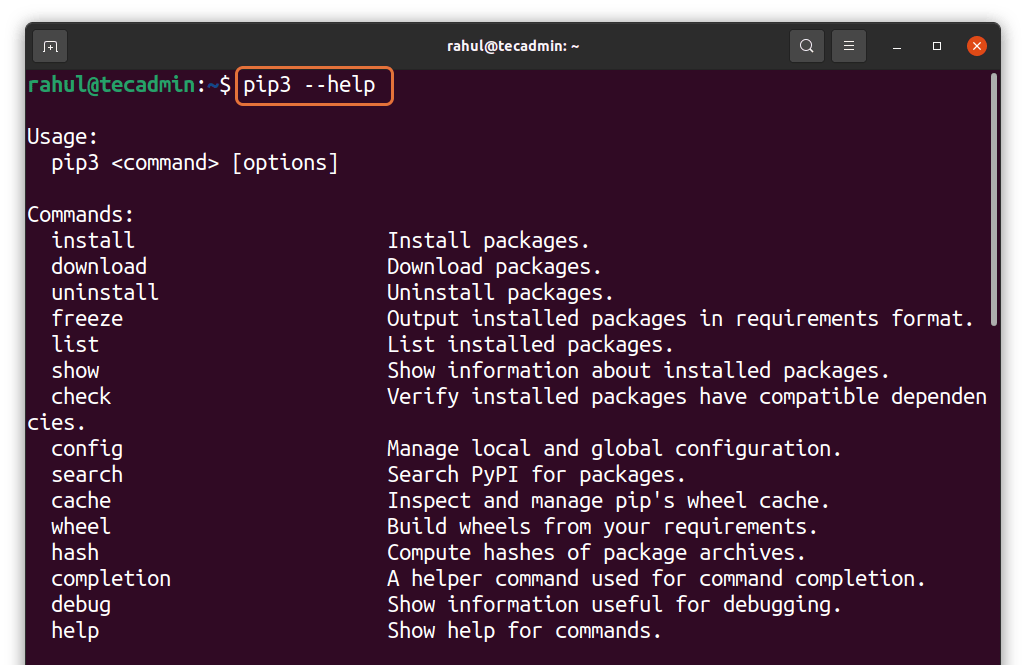
Now, if you want to know how to use the pip command and what are the available features then you can see them by typing the following command in the terminal.
pip --help
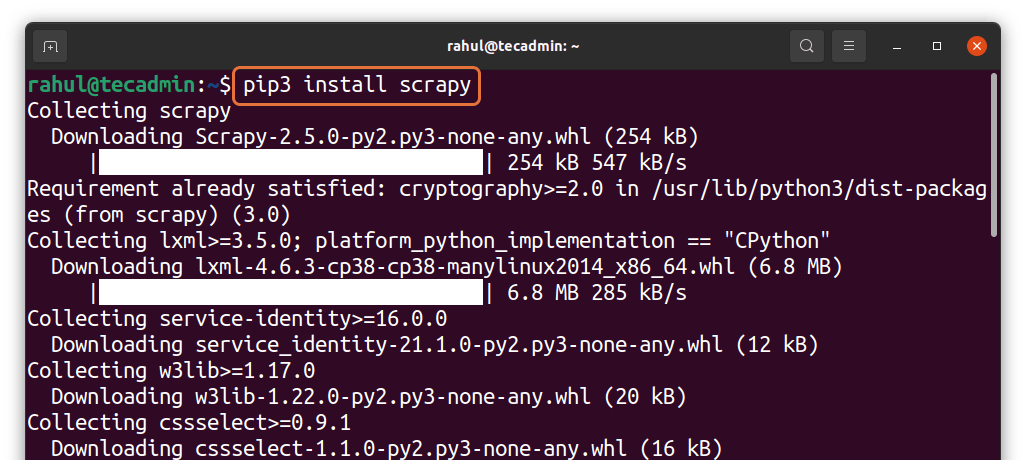
Now as you can see from the above image, the first command is to install the packages. So let us take an example of installing the “scrapy” python package. You can do that by typing:
pip3 install scrapy
You can install any other package of your choice as well by following the exact same syntax.
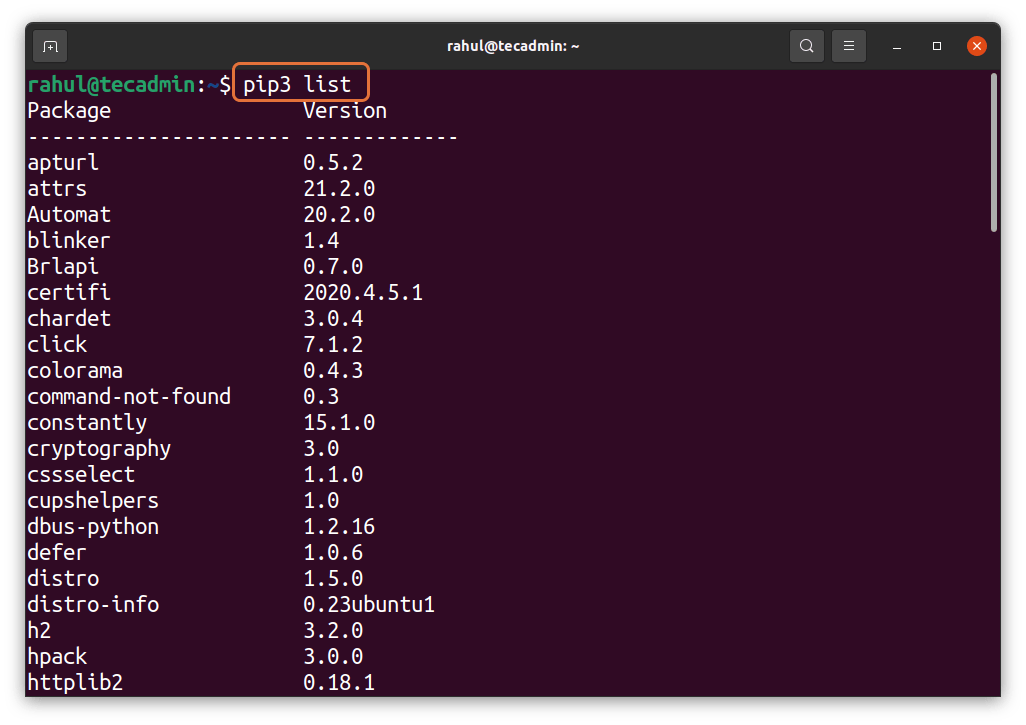
After installation, you can check if the package is installed or not by typing the following command in the terminal.
pip3 list
This command will show you the list of all installed packages and you may need to scroll down to find your installed packages.
How to Uninstall the Python packages
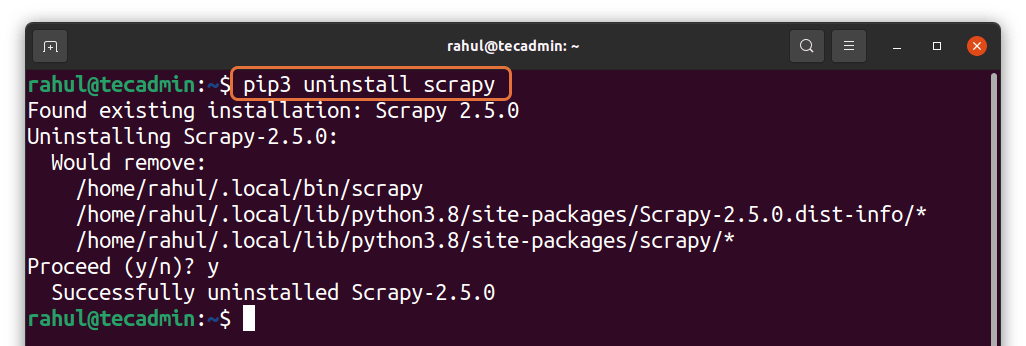
You can uninstall any previous package that you have installed by typing
pip3 uninstall scrapy
The scrapy package has been installed.
How to Install PIP for Python 2
The pip package for python 2 is present in universe repository but if you don’t have in your system then to install it use:
sudo add-apt-repository universe
Now, use the command mentioned below to update the packages list:
sudo apt update
Install the Python2 minimal package first.
sudo apt install python2-minimal
The Pip packages for Python2 is not included in Ubuntu 20.04. So we need to use pip installer script.
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
Then execute the Python script with python2 to install Pip on your system.
sudo python2 get-pip.py
After the installation you can check the version by typing:
pip2 --version
Output:pip 20.3.4 from /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pip (python 2.7)
How to Uninstall PIP from Ubuntu 20.04
If you want to uninstall the pip package for python 3, then you can do that by typing the following commands in the terminal:
For python 3:
sudo apt purge python3-pip
Conclusion
Python is the most simplified and easy-to-learn programming language. Python codes are faster to execute and have tons of modules to work with to enhance the functionality of the programs. This article has shown you how you can install pip packages for python 2 and python 3 for Ubuntu OS 20.04. Moreover, we also learned how to uninstall a package and pip.