Certbot is a command-line utility for managing Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates on a Linux system. It allows you to request a new SSL certificate, do the authorization and configure your web server for SSL settings. It also helps you to renew certificates issued by the Let’s Encrypt certificate authority.
This tutorial helps you to install and use Certbot (A Let’s Encrypt client) on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Linux system.
Prerequisites
You must fulfill the followings:
- A running Ubuntu 20.04 system with sudo privileged account access.
- Apache web server with virtual host configured with a real domain or subdomain.
- Domain or sub-domain must be pointed correctly to web server IP address.
Step 1 – Installing Certbot
Certbot is a tool to obtain certificates from Let’s Encrypt and configure them on your web server. The Snap package is the easiest way for installing the certbot on the Ubuntu system.
Open a terminal and execute the below command to install certbot:
sudo snap install --classic certbot
Step 2 – Generate SSL Certificate
Now, You can request SSL certificates from Let’s encrypt based on the web server.
- Apache – The systems running Apache web server, execute the following command. This will list all the domains/sub-domains configured on your web server. Select appropriate numbers to request a certificate.
sudo certbot --apache - Nginx – For the systems running Nginx web server, use below command to request for the SSL certificates.
sudo certbot --nginx - Get Certificate Only – For the system having any other web servers running except Apache or Nginx. Then you can get the certificate only and configure them manually.
This command will ask you for the domain name and document root for the domain.
sudo certbot certonly --webroot - No Web Server – The systems have no web server running, can also request a SSL certificate. The below command will ask you for the domain name and start a temporary web server on port 80 to complete the verification.
sudo certbot certonly --standalone
While using the above commands, the domain must be pointed to the server in DNS. Also, ensure that /.well-known/acme-challenge is served by the web server.
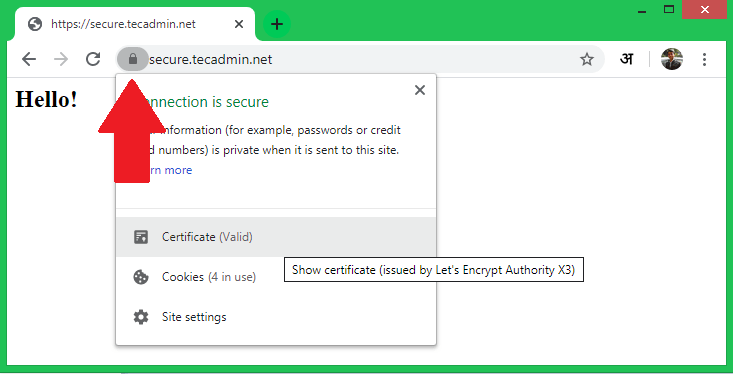
Step 3 – Test SSL
Once the SSL certificate is installed on the web server, visit https://your-domain.com/ in a web browser and look for the SSL lock icon in the URL bar. You can also do a security scan for the SSL setup on https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/.
Step 3 – Renew SSL Certificate
A Let’s Encrypt certificate is issued for the 3 months only. You need to renew the certificate before 30 days of expiry. Certbot allows you a hassle-free renewal just by running a single command.
Run the below command to renew all the certificates on that system.
sudo certbot renew
You can also run a dry run without actual renewal. This will help you to test if SSL renewal performs well.
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned to install certbot on the Ubuntu system. Also helped you to create new certificates for your web servers.

5 Comments
Here it says: “Certbot has set up a scheduled task to automatically renew this certificate in the background.”.
Now I’m in doubt.
Do I need to set up a task on crontab to automatically run “sudo certbot renew” command?
Thank you for the nice post!
Posso executar esse comando para que a renovação aconteça de forma automática sem intervenção humana?
0 2 * * * sudo / usr / sbin / certbot-auto -q renew
Desde já agradeço
Yes, Just make sure the certbot binary path is correct
0 5 * * * /snap/bin/certbot renew –quiet
thanks very much!