Django is a Python Web framework that encourages rapid development of applications. This tutorial helps you to install Django on Debian 10 Buster, Debian 9 Stretch system. After that create and run your first Django applications.
Step 1 – Prerequsities
The latest versions of operating systems come with default Python 3 installed. The minimal installation systems may not have Python installed, Execute the below commands to install it. Also, install pip on your system.
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip
Then check the Python and pip version:
python3 -V Python 3.5.3
pip3 -V pip 9.0.1 from /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (python 3.5)
Step 2 – Install Django on Debian
Django source code is available as a Github repository. You can also use pip to install Django on Debian 9 systems. In this tutorial, I use pip3 for the Django installation on Ubuntu. Run the below command from Linux terminal:
pip3 install Django
You will get a django-admin command for creating new projects. Check the current installed verson:
django-admin --version 2.1.2
Step 3 – Create Django Application
The django-admin command provides you the option to create a new Django application via command line. First, navigate to the directory you need to create a new application.
Then use the django-admin startproject command followed by the application name to create a new Django application on a Debian Linux.
cd /var/www django-admin startproject django_app
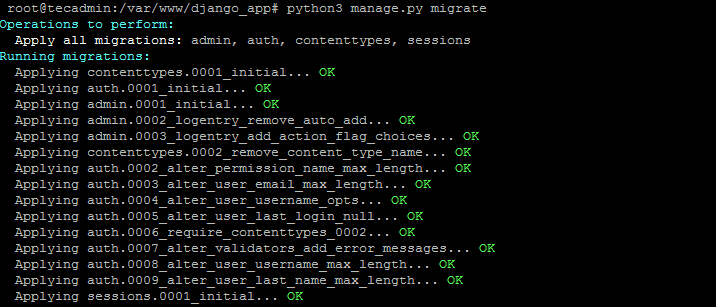
After that migrate the pending changes.
cd django_app python3 manage.py migrate
Step 4 – Create Super Admin Account
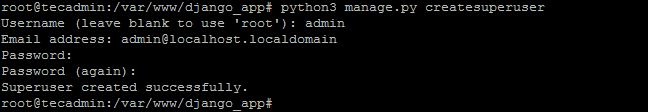
Also, create a superuser account for the administration of the Django application. Run the following command from your Django application directory.
python3 manage.py createsuperuser
Make sure all the migrations completed successfully. Once done, go to the next step.
Step 5 – Run Django Application
Your Django application is ready to use. By default, Django doesn’t allow external hosts to access the web interface. To allow external hosts, edit settings.py file and add IP under ALLOWED_HOSTS.
vi django_app/settings.py
Add IP:
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['192.168.1.239']
Here 192.168.1.239 is the IP address of the system where Django is installed.
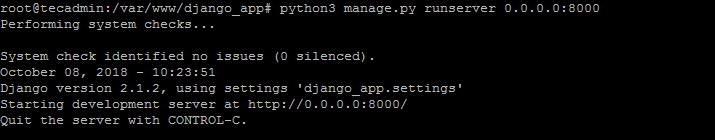
Finally, run the Django application server with the below command. Here 0.0.0.0:8000 defined that Django will listen on all interfaces on port 8000. You can change this port with any of your choices.
python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
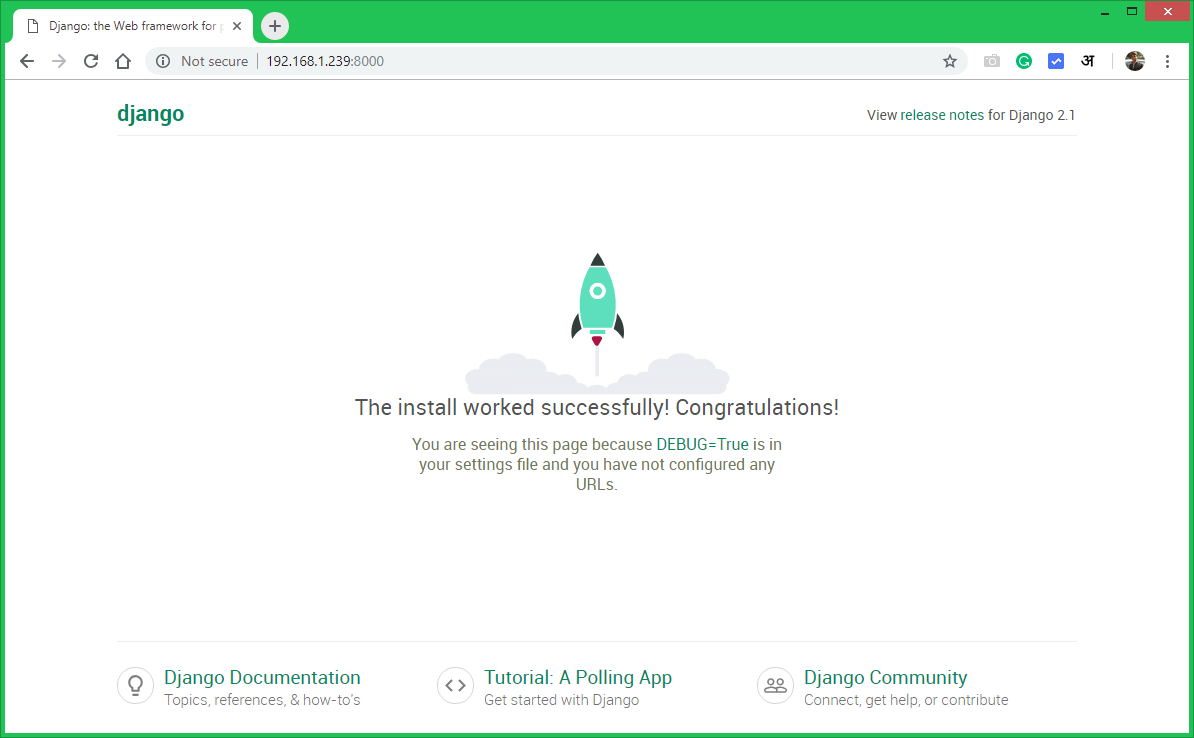
The Django application server is running now. Open your favorite web browser and access to Django system IP on port 8000. This will show you the default Django web page.
http://192.168.1.239:8000
Django also provides an administrative web interface. You can access this at /admin subdirectory URL of your Django application. Use superuser login credentials created in the previous step.
http://192.168.1.239:8000/admin
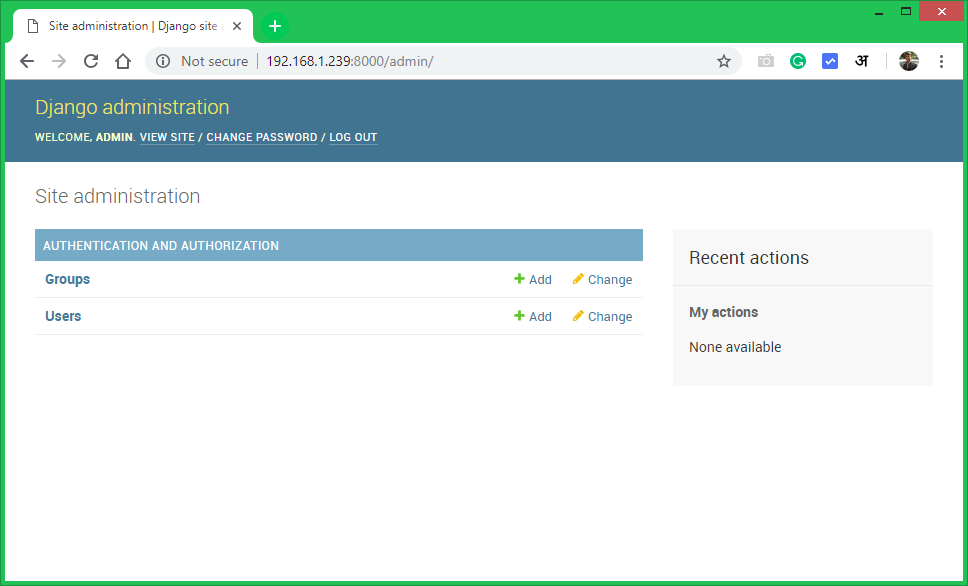
The Django admin dashboard looks like below. Here you can add more users and groups for your application.

5 Comments
Hello ,
thanks for this tutorial.
I would like to assign django to a site http://www.example.com: 8000 and not to an ip address.
I’m on Debian 9 (Stretch) + ISPConfig 3
thank you
i am gettin django.db.utils.OperationalError: attempt to write a readonly database what should do i ?
*sudo pip3 install Django
What is default password?
user name: admin
password: what is default?
The password you entered in step 4.