VPN or Virtual Private Network is a group of computers connected to the private network over the public network (Internet). These days security is the primary concern for everyone and it’s more required while working over the public network.
Like you have a group of computers in a remote location. Now you need to access those computers as a LAN network in your system. Also, you need all data should be encrypted during transfer between computers. The solution is a VPN. You can use a VPN network to connect two remote location systems with each other as they are on the same LAN. This tutorial will help you to install and configure the OpenVPN server on Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint systems.
Step 1 – Prerequisites
Login to your Ubuntu system using SSH. Now update system’s apt cache and update your system packages to latest versions.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2 – Install OpenVPN Server
Now, Install the OpenVPN package by typing below command. Also, install
sudo apt-get install openvpn easy-rsa
Copy the sample configuration file for OpenVPN to /etc/openvpn/server.conf file. This will be used as an OpenVPN server configuration file.
gunzip -c /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz > /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Step 3 – Configure OpenVPN Server
Edit the OpenVPN server configuration file in your favorite text editor.
vim /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Remove the “;” to uncomment lines or add new lines for the following entries in the configuration file.
tls-auth ta.key 0 key-direction 0 cipher AES-256-CBC auth SHA256 comp-lzo user nobody group nogroup cert server.crt key server.key
The above settings will allow VPN connection between systems. But they will not direct the client’s internet traffic through VPN. Also, uncomment the dhcp-option values.
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222" push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"
Step 4 – Update Network Configuration
Do some network settings to allow users to access the server on the same network of OpenVPN servers. First, Allow IP forwarding on the server by executing the below commands to set
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf sudo sysctl -p
Masquerade the internet traffic coming from the VPN network (10.8.0.0/24) to systems local network interface (eth0). Where 10.8.0.0 is my VPN network and eth0 is the network interface of my system.
sudo modprobe iptable_nat sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
Step 5 – Setup Certificate Authority
OpenVPN provides secure VPN service using TLS/SSL encryption of traffic between server and client. For this, you need to issue trusted certificates for servers and clients to work. To issue certificates you need to configure Certificate Authority on your system.
Let’s create a directory for certificate authority using
make-cadir /etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca/ cd /etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca/
Edit
vim vars
and update the below values as required. These values will be used as default values to issues the certificates for servers and clients. You can also overwrite these values during certificate creation.
export KEY_COUNTRY="US" export KEY_PROVINCE="CA" export KEY_CITY="SanFrancisco" export KEY_ORG="TecAdmin" export KEY_EMAIL="[email protected]" export KEY_OU="Security"
Load the values in system environment.
source vars
Now use
./clean-all ./build-ca
Sample output of above command:
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ...+++ ..........................................+++ writing new private key to 'ca.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [US]: State or Province Name (full name) [CA]: Locality Name (eg, city) [SanFrancisco]: Organization Name (eg, company) [TecAdmin]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Security]: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [TecAdmin CA]: Name [EasyRSA]: Email Address [[email protected]]:
Now your system is ready as Certificate Authority to issue the certificates.
Step 6 – Generate Server Certificate Files
Firstly create the certificates for the OpenVPN server using the
cd /etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca/ ./build-key-server server
Sample output of above command:
... ... Signature ok The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows countryName :PRINTABLE:'US' stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'CA' localityName :PRINTABLE:'SanFrancisco' organizationName :PRINTABLE:'TecAdmin' organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'Security' commonName :PRINTABLE:'server' name :PRINTABLE:'EasyRSA' emailAddress :IA5STRING:'[email protected]' Certificate is to be certified until Jan 2 05:33:24 2028 GMT (3650 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated
Now generate a strong Diffie-Hellman key to use for the key exchange using the command. This command may take some time to complete.
openssl dhparam -out /etc/openvpn/dh2048.pem 2048
After that generate an HMAC signature to make more secure TLS integrity verification capabilities of the server.
openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca/keys/ta.key
After creating all files, copy them to
cd /etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca/keys sudo cp ca.crt ta.key server.crt server.key /etc/openvpn
Step 7 – Start OpenVPN Service
OpenVPN server is ready now. Let’s start the service using the systemctl command. Also, Check the status of service.
sudo systemctl start openvpn@server sudo systemctl status openvpn@server
On the successful start of service, you will see results like below.
● [email protected] - OpenVPN connection to server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/[email protected]; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-01-04 11:09:51 IST; 6s ago Docs: man:openvpn(8) https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/Openvpn23ManPage https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/HOWTO Process: 4403 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-%i --status /run/openvpn/%i.status 10 --cd /etc/openvpn -- Main PID: 4404 (openvpn) CGroup: /system.slice/system-openvpn.slice/[email protected] └─4404 /usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-server --status /run/openvpn/server.status 10 --cd /etc/openvpn -- Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: /sbin/ip addr add dev tun0 local 10.8.0.1 peer 10.8.0.2 Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: /sbin/ip route add 10.8.0.0/24 via 10.8.0.2 Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: GID set to nogroup Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: UID set to nobody Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef] Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: UDPv4 link remote: [undef] Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: MULTI: multi_init called, r=256 v=256 Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: IFCONFIG POOL: base=10.8.0.4 size=62, ipv6=0 Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: IFCONFIG POOL LIST Jan 04 11:09:51 laitkor237 ovpn-server[4404]: Initialization Sequence Completed
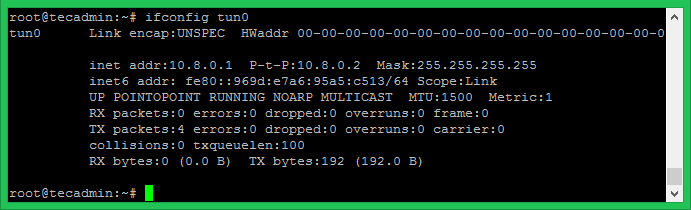
OpenVPN will create a network interface name
ifconfig tun0
Step 8 – Generate Client Configuration
You OpenVPN server is ready to use. Now generate the client configuration files including the private key, certificates. I have made this process easier for you to generate any number of configurations files using a simple script. Follow the below steps to generate configuration files. Make sure to use correct directory structure.
mkdir /etc/openvpn/clients cd /etc/openvpn/clients
Create a shell script file as below.
vim make-vpn-client.sh
copy the below content. Update the
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | #!/bin/bash # Generate OpenVPN clients configuration files. CLIENT_NAME=$1 OPENVPN_SERVER="192.168.1.237" CA_DIR=/etc/openvpn/openvpn-ca CLIENT_DIR=/etc/openvpn/clients cd ${CA_DIR} source vars ./build-key ${CLIENT_NAME} echo "client dev tun proto udp remote ${OPENVPN_SERVER} 1194 user nobody group nogroup persist-key persist-tun cipher AES-128-CBC auth SHA256 key-direction 1 remote-cert-tls server comp-lzo verb 3" > ${CLIENT_DIR}/${CLIENT_NAME}.ovpn cat <(echo -e '<ca>') \ ${CA_DIR}/keys/ca.crt \ <(echo -e '</ca>\n<cert>') \ ${CA_DIR}/keys/${CLIENT_NAME}.crt \ <(echo -e '</cert>\n<key>') \ ${CA_DIR}/keys/${CLIENT_NAME}.key \ <(echo -e '</key>\n<tls-auth>') \ ${CA_DIR}/keys/ta.key \ <(echo -e '</tls-auth>') \ >> ${CLIENT_DIR}/${CLIENT_NAME}.ovpn echo -e "Client File Created - ${CLIENT_DIR}/${CLIENT_NAME}.ovpn" |
Set the execute permission on the newly created script.
chmod +x ./make-vpn-client.sh
Now use this script to generate configuration file for the VPN clients including certificates and keys. You need to pass client name as command line parameter.
./make-vpn-client.sh vpnclient1
Press enter for the default values of the certificate. At the end, it will prompt for the sign the certificate and commit. Press y for both inputs.
Certificate is to be certified until Jan 2 07:18:10 2028 GMT (3650 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base UpdatedClient File Created - /etc/openvpn/clients/vpnclient1.ovpn
The above script will create client configuration file under /etc/openvpn/clients/ directory with client name with .ovpn extension as shows in last line of output. Use this file to connect from remote systems.
Step 9 – Connect VPN from Clients
You need the configuration file generated from above
Windows Clients
Download OpenVPN GUI client software from its official download page and install on your system. Now copy the given .ovpn file under
Linux Clients
On Linux clients, First, you need to install OpenVPN packages. After that use the following command to connect to the OpenVPN server using the given client configuration file.
openvpn --config client1.ovpn
After successfull connection OpenVPN will assign an IP address to your system. Use following command to check assigned IP address.
ifconfig tun0
[output]
tun0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00
inet addr:10.8.0.18 P-t-P:10.8.0.17 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)

20 Comments
“source vars”, results in:
You appear to be sourcing an Easy-RSA ‘vars’ file.
This is no longer necessary and is disallowed. See the section called
‘How to use this file’ near the top comments for more details.
time to update?
Not able to access internet on vpn server
# all IP traffic such as web browsing and
# and DNS lookups to go through the VPN
# (The OpenVPN server machine may need to NAT
# or bridge the TUN/TAP interface to the internet
# in order for this to work properly).
comment this line (;push “redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp”)
This one works for copying sample conf. gunzip -c /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz | sudo tee /etc/openvpn/server.conf
please update this page.
can not connect the client to the server .. I get a TLS error. However, I took the same configuration more than 20 times … need help
please check at ovpn config
It is perfectly working. Thank you
Great job Rahul. Did setup my openvpn-server on my ubuntu server 9.000 kilometers away with your manual in 10 min. Works as a charm.
My ubuntu server is located at my friends house and is behind a NAT router. We have forwarded a ssh port in the router so I can access my baby.
1 thing I was confused about:
“Update the OPENVPN_SERVER variable with the correct OpenVPN server ip address and save it.”
My device is the openvpn-server but his ip address is not the one we need. We do need to fill in the external ip-adres of the router.
Thansk for your effort!
Hi,
I have correctly configurat my openvpn, and created clients, it works .
How to revocated old a client ?
Sorry for mi bad english, je ne suis qu’un petit français.
;o)
Hello
Thanks for the tutorial its working fine with the linux system but i am trying to use same file on windows i get following error
Mon Jan 07 13:23:10 2019 NOTE: –user option is not implemented on Windows
Mon Jan 07 13:23:10 2019 NOTE: –group option is not implemented on Windows
Options error: –up script fails with ‘/etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf’: No such process (errno=3)
Options error: Please correct this error.
Use –help for more information.
Thanks, i am only able to connect my VPN server not other server.
my network is 10.4.14.0/24, 10.4.18.0/24 & 10.4.20.0/24
Please help me to provide the right configuration for above subnet. thanks
hi, thanks for this wonderful tutorial. i need help !!
my private subnet is 10.4.14.0/24, 10.4.18.0/24, 10.4.20.0/24
what configuration i need to update in server.conf to connect my private network. Please help !!
Thanks.
Hi, who yo remover the client?
Do you have how to configure openvpn for IPV6 …
its suggested you disable ipv6 for your VPN. I’ve read this from numerous sources online. unfortunately there is not one single complete VPN tutorial on the internet I have found. Every tutorial leaves out some important detail. Also, so far, any tutorial claiming to be teach you how to set on VPN server on Ubuntu 18.04 is a complete joke. It’s as if the author just changed the title in order to try to gain traffic to their website without even trying to get a VPN running on Ubuntu 18.04
I got it to the last step but i get this messange and then it tries to reconnect :
TLS key negotiation failed to occur within 60 seconds (check your network connectivity)
TLS Error: TLS handshake failed
I can’t pass step 3, I get a bash message : permission denied. What do you think I could do?
Run
`sudo su`
and type in the root password.
This will force the terminal into a root terminal so that you can do everything you need to without getting those stupid errors.
Thanks for this tutorial man! Stay awesome!
I have successfully configured OpenVPN server on my Ubuntu box. Thanks for awesome tutorial.