ownCloud is a software application provide self hosted file hosting services. You can install owncloud application on your server and use it as your own file server. Where you can easily upload/sync files from the client machine. It also provides options to sync and share across devices—all under your control. This tutorial will help you to set up your own file hosting server with the ownCloud on Debian 10 Buster Linux system.
Prerequsites
- Shell access to Debian 10 Linux system
- Sudo privilege account access
Step 1 – Install LAMP
The first of all, to set up ownCloud you must have running LAMP server on your Debian 10 system. If you already have running LAMP stack skip this step else use the following commands to install it.
Install PHP
Let’s start with the installation of PHP 5.6 or higher version on your Debian 10 Buster Linux system.
wget -q https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg -O- | sudo apt-key add - sudo echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ buster main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list
sudo apt update sudo apt install php-gd php-curl php-zip php-dom php-xml php-simplexml php-mbstring php-intl php-json
Install Apache2
sudo apt-get install -y apache2 libapache2-mod-php
Install MySQL
sudo apt-get install -y mysql-server php-mysql
Step 2 – Download ownCloud Source
After successfully configuring lamp server on your system, Let’s download latest ownCloud from its official website.
cd /tmp wget https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-10.4.0.tar.bz2
Now extract downloaded archive under website document root and setup appropriate permissions on files and directories.
cd /var/www/html sudo tar xjf /tmp/owncloud-10.4.0.tar.bz2 sudo chown -R www-data:www-data owncloud sudo chmod -R 755 owncloud
Now, remove the archive file.
sudo rm -f /tmp/owncloud-10.4.0.tar.bz2
Step 3 – Create MySQL Database and User
After extracting code, let’s create a MySQL database and user account for configuring ownCloud. Use following set of command to login to MySQL server and create database and user.
mysql -u root -p Enter password: mysql> CREATE DATABASE owncloud;mysql> GRANT ALL ON owncloud.* to 'owncloud'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '_password_';mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;mysql> quit
Step 4 – Install ownCloud with Web Installer
Now access the ownCloud directory on a web browser as below. Change localhost to your server IP address or domain name.
http://localhost /owncloud/
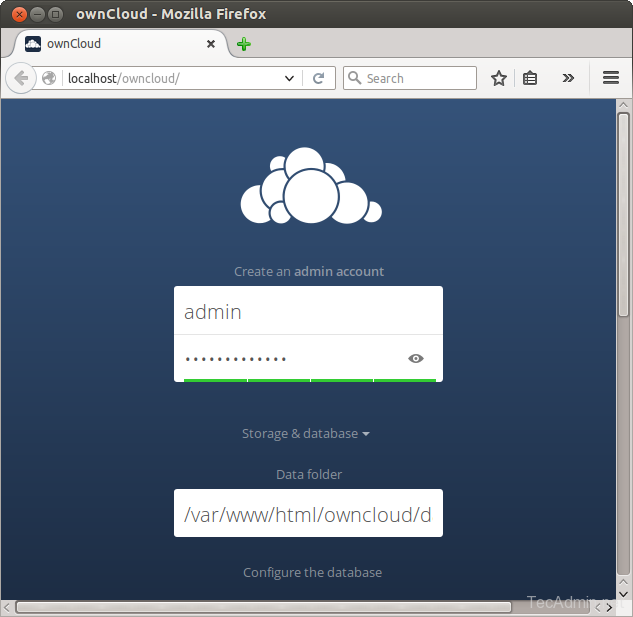
Enter new admin credentials to create an admin account and provide the location of the data folder.
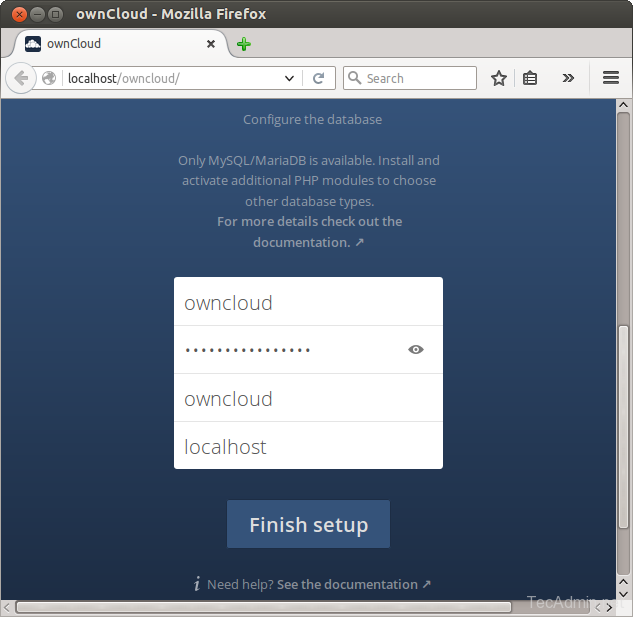
Now slide your page down and input the database credentials and click on Finish Setup.
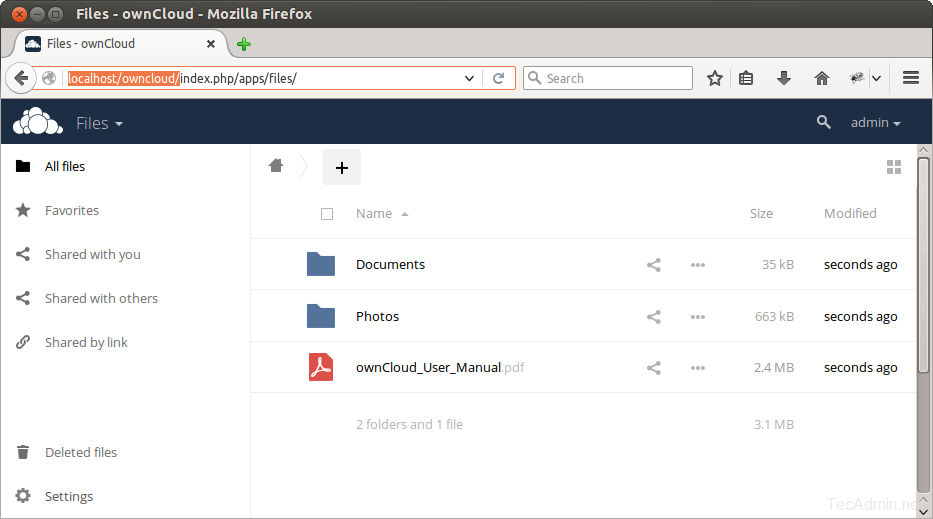
After completing setup you will get the admin dashboard. Where you can create a user, groups, assigned them permissions, etc.
Conclusion
Congratulations, You have a working ownCloud instance on your Debian 10 Buster Linux system.