Parse Server is an open source application written on node.js programming language. The parse application is used as the Backend As A Service (BAAS) platform. Which helps developers to build their mobile application’s back-end.
Parse dashboard is another application built on node.js by the parse developers. It is an front-end web interface for managing backend parse server. You can add and manage multiple parse server from single dashboard.
This tutorial will help you to install and configure parse server and parse dashboard applications on Ubuntu system.
Prerequisites
- Setup a sudo privileged account and apply initial security by following initial server setup
- Login to instance via SSH as root account
Step 1 – Installing Node.js
The Parser server and dahsboard are build on node.js platform. So you need to install Node.js on your Ubuntu system. You can use official packages repository to install it. To configure apt repository, execute:
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_12.x | sudo -E bash -
The run the following commands to install Node.js on your server.
sudo apt install -y nodejs
Also install yarn package manager on your system. This will be used for install node modules.
npm install -g yarn
Step 2 – Installing MongoDB
The Mongodb packages are available under the default apt repositories. You can simply update apt cache and install Mongodb database server packages by running following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt install mongodb-server
Step 3 – Install Parse Server
Your Ubuntu system is ready for the Parse server installation. The parse server available as nodejs modules. Use the following command to install parse-server module using yarn package manager:
yarn global add parse-server
Next create a configuration file for your Parse server. Where you can define attributes of the parse server. Create a configuration file and edit in your favorite text editor:
nano config.json
Then, add the following content to the file:
{
"appName": "My Parse Server",
"databaseURI": "mongodb://localhost:27017/parsedb",
"appId": "KSDJFKASJFI3S8DSJFDH",
"masterKey": "LASDK823JKHR87SDFJSDHF8DFHASFDF",
"serverURL": "https://localhost:1337/parse",
"publicServerURL": "https://0.0.0.0:1337/parse",
"port": 1337
}
Configuration details:
Save your file. Next run the parse server with nohup command. Also run it as background process.
nohup parse-server config.json &
Your parse server is up and running now on port 1337.
Step 4 – Setup Parse Dashboard
The Parse development team, also provides a web interface to access Parse server called Parse-dashboard. Which is also available as node module. Use below command to install parse-dashboard:
yarn global add parse-dashboard
Next, create a configuration file for the parse dashboard. Edit file in a text editor:
nano parse-darshboard-config.json
And add the following content:
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://67.205.146.114:1337/parse",
"appId": "KSDJFKASJFI3S8DSJFDH",
"masterKey": "LASDK823JKHR87SDFJSDHF8DFHASFDF",
"allowInsecureHTTP": "true",
"appName": "MyApp1"
}
],
"users": [
{
"user":"admin",
"pass":"password"
}
],
"iconsFolder": "icons"
}
You can add multiple parse servers to your Parse dashboard. Add your parse server with serverURL. User the same appID and masterKey as you defined to your parse server.
Save your file and execute the following command to start parse dashboard.
nohup parse-dashboard --dev --config parse-darshboard-config.json &
The above command will start your parse server on port 4040.
Step 5 – Open Ports in FirewallD
The systems have enabled firewalld, need to allow access on ports running Parse server. We are using the port 1337 for the parse server and 4040 for the dashboard. Execute the following commands to allow access for public users for Parse server. To open port type:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=1337/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=4040/tcp
Apply the changes by running command:
firewall-cmd --reload
Step 6 – Test Setup
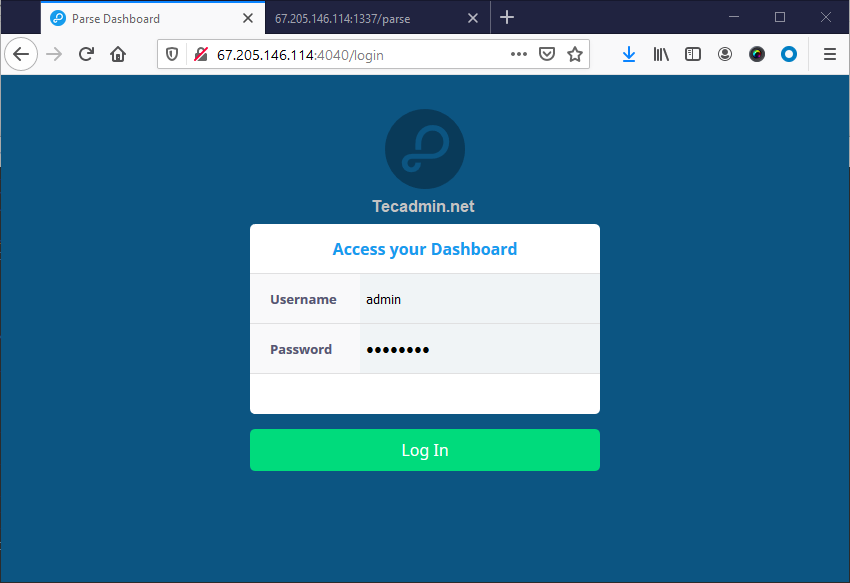
Now, you can access your parse dashboard web interface by accessing your server on port 4040. Login to the dashboard username and password defined in parse dashboard configuration file (parse-darshboard-config.json).
After login you will see the dashboard.
Conclusion
In this tutorial you learned about the installation of parse server and dashboard on Ubuntu system.
4 Comments
I followed these instructions, and is works OK, but everytime I restart the server I have to issue the commands
nohup parse-server config.json &
then Crtrl-C out of that and then enter
nohup parse-dashboard –dev –config parse-darshboard-config.json &
Does anyone have any idea how to get it to start automatically after a server reboot?
How to add LiveQuery function on this installation?
Hello. And Bye.
Thank you pretty much for sharing the massive information to us. It
is very useful and informative.
Please keep blogging new updates.
Thanks