The wget command in Linux is a powerful tool for downloading files from the internet. It allows you to download files from a URL and save them to your local file system. This command-line utility can be used to download single files, entire directories, or even complete websites. Whether you need to download files for backup purposes, or to transfer large files between systems, the wget command is an indispensable tool for any system administrator.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the wget command, including its various options and how to use it effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned Linux veteran or a newcomer to the platform, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential command.
Installing Wget in Linux
Generally, the wget package is pre-installed on Linux distributions. But in some cases of minimal installations, It may not be installed.
Open a terminal and execute the following commands to install or upgrade the Wget package from the default package manager.
- On Ubuntu, Debian & Linux Mint Systems
sudo apt update && apt install wget -y - On CentOS, RHEL & Fedora Systems
sudo dnf install wget -y
Wget Command Syntax
A simple Wget command follows the below syntax.
wget [option]... [URL]...
A large number of command-line options make it more usable. Wget uses GNU getopt to process command-line arguments, which means all options have a long form along with a short one.
Wget required a URL to an archive, IOS, or webpage to download.
Wget Command Examples
Here are some frequently used wget commands with examples.
1. Downloading a file
Open a terminal and type wget followed by the remote file URL to download on the local machine. No additional parameters are required to download a file.
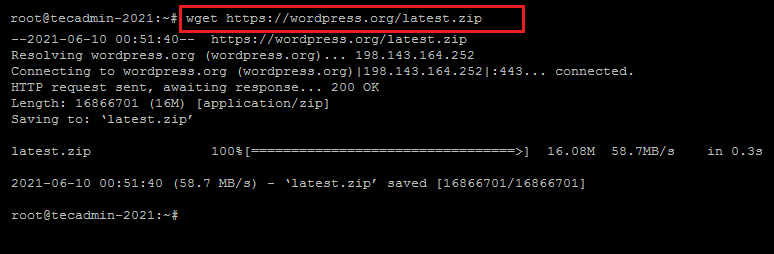
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.zip
The above command will download the file in the current working directory. The filename will remain the same in the local system as on the remote machine.
2. Download file with a new name
Default wget downloads the file with the same name on the local system. Use -O (Capital O) command-line option followed by a new name to write a file on the local system.
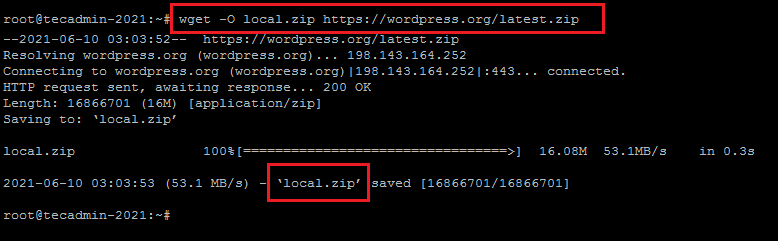
wget -O local.zip https://wordpress.org/latest.zip
See the below screenshot, showing the local file is created with a new name.
3. Download Large files with resume option
The Wget allows us to resume downloading a partially downloaded file. It is helpful for downloading large files from a remote. In any case, the download interrupts and can resume downloading the remaining content only instead of a full download.
Use -c or --continue to switch with the file.
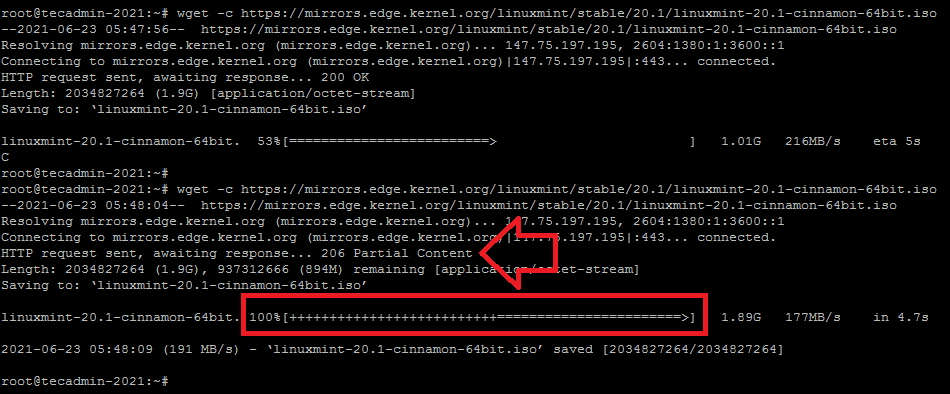
wget -c //mirrors.edge.kernel.org/linuxmint/stable/20.1/linuxmint-20.1-cinnamon-64bit.iso
See the below example, Downloading a large file with the -c option. In the first attempt, once the downloading started killed the download process with CTRL+C. Now again execute the same command and you can see the downloading resumes.
4. Execute remote scripts without creating local file
Wget is also widely used for executing remote scripts through scheduled jobs like crontab. But we found that it creates a new file with each run under the home directory. We can instruct wget to redirect all content to /dev/null and ignore creating files.
wget -q -O /dev/null https://google.com
Here -q will suppress all the output on-screen and -O will redirect all the content to /dev/null file.
5. Creating a mirror of the website
Wget allows us to download website content recursively. It follows the internal links available in HTML content. Use --recursive option with the wget command to download the entire site in your local system.
wget --recursive https://google.com
You can also set the maximum depth for recursion with the -l option.
wget --recursive -l 2 https://google.com
The above commands will create a directory with the same name as the domain in the current directory and place all files under it.
6. Downloading files in the background
To download a file in the background, use the -b or --background option.
wget -b https://example.com/file.zip
7. User authentication with wget requests
Most of the files over remote FTP servers are secured with authentication. In some cases, content over the HTTP can be secured with authentication. Wget allows us to pass authentication details with this request.
wget --user=USER --password=PASS https://example.com/backup.zip
You can use --user and --password for both FTP and HTTP authentications.
8. Download files with a specific extension
To download only files with a specific extension, use the -A or --accept option. For example to download all PDF files from a website.
wget -r -A .pdf https://example.com
Conclusion
The wget command is a versatile and powerful tool that every system administrator should be familiar with. Whether you need to download files for backup purposes, or to transfer large files between systems, the wget command provides an easy and efficient way to do so. With its many options and customizable features, it’s a must-have tool for anyone who works with Linux. Whether you’re a seasoned Linux veteran or just starting out, this guide has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the wget command, and how to use it effectively.

