Systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems. It is widely used to manage services, network interfaces, and other system resources on Linux-based servers. In this tutorial, we’ll explain how to run a PHP script as a systemd service on Linux.
To create a systemd service for a PHP script, you’ll need to create a unit file that describes the service’s configuration. The unit file generally saved in the /etc/systemd/system directory and should have a .service file extension. This tutorial will help you to create a systemd service for your PHP script.
Step 1: Create the PHP Script
First, create the PHP script that you want to run as a systemd service. For example, let’s create a simple script named myscript.php which simply write the currently date and time in a log file. Which will help us to easily understand the execution times.
<?php
// Set the script to run indefinitely
while (true) {
$logFile = '/opt/scripts/script.log';
$currentTime = date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
file_put_contents($logFile, "Script running at: $currentTime\n", FILE_APPEND);
sleep(10);
}
?>
Save this file in a directory of your choice, such as “/opt/scripts”.
Step 2: Create the Systemd Unit File
Next, create the systemd unit file for the PHP script. This file will define the service’s configuration, such as its name, description, and how it should be started and stopped. Create a file called “myscript.service” in the “/etc/systemd/system” directory:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/myscript.service
Add the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=My PHP Script Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/bin/php /opt/scripts/myscript.php
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
User=www-data
Group=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/opt/scripts
Environment="ENV_VAR=production"
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=journal
ExecStop=/bin/kill $MAINPID
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
This unit file tells systemd to create a service called myscript that runs the myscript.php script using the PHP interpreter. It also specifies that the service should be restarted automatically if it fails for any reason.
Step 3: Reload the Systemd Configuration
Once you’ve created the unit file, you need to reload the systemd configuration to make it aware of the new service. You can do this by running the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Step 4: Start and Enable the Service
Finally, you can start the “myscript” service by running the following command:
sudo systemctl start myscript
You can also enable the service to start automatically at boot time by running the following command:
sudo systemctl enable myscript
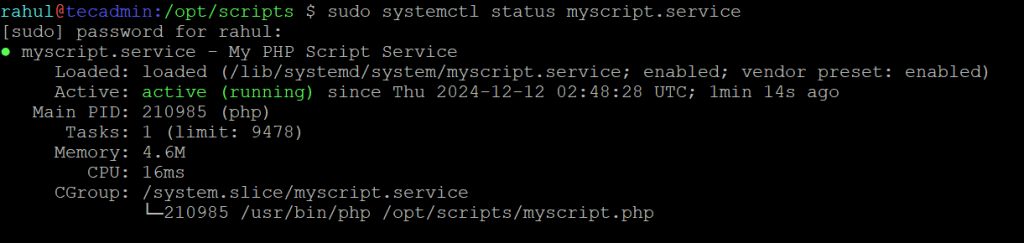
To check the status of the service, you can run the following command:
sudo systemctl status myscript
This will show you whether the service is running, whether it has failed, and any recent log output.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve shown you how to create a systemd service for a PHP script on Linux. By following these steps, you can run a PHP script as a systemd service and ensure that it starts automatically at boot time, restarts if it fails, and is easily manageable with the systemctl command. This can be useful for running PHP scripts that need to run continuously in the background, such as daemons, cron jobs, or long-running processes.