Being a software developer or system administrator, you may have need to work with multiple Git repositories from the differnet-2 account. For example, you may have multiple Github accounts, Gitlab, Bitbucket or AWS Codecommit accounts for the projects. If you are using http/https protocol to access git repositories, may face issues with the authentication. In this situation, ssh based access is the best option to access repositories.
This tutorial will help you to configure you Unix/Linux system to connect multiple Git account with ssh key pare based access.
Step 1 – Generate New SSH keys
First of all, check for all the available SSH keys in your account. Type: ls -l ~/.ssh to list all key pairs, So you won’t overwrite any key with below commands.
Let’s create first key pair by typing below command.
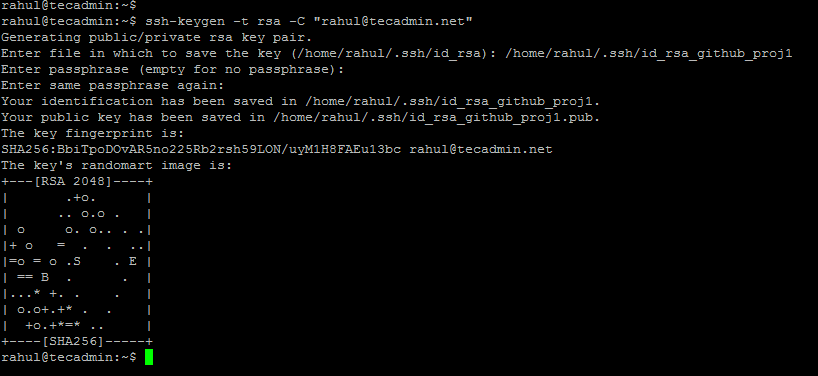
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your-email"
- Execute above command with your email address.
- Set a new file path to prevent override existing file as: /home/rahul/.ssh/id_rsa_github_proj1
- Press enter for passphrase and confirm passphrase to keep it empty
- Your key is ready.
The above command will create two file under ~/.ssh directory. Once is private key and one is public key.
- Private key: ~/.ssh/id_rsa_github_proj1 (Never share this file with anyone)
- Public key: ~/.ssh/id_rsa_github_proj1.pub (Upload this file to your Git account)
Use the above command to create more SSH key pairs. Just remember to change the filename to prevent overwrite of file.
Step 2 – Attach SSH keys to Git Accounts
Now add the SSHs key to the corresponding GitHub, Gitlab, AWS Codecommit and other Git accounts. Copy the .pub file content and upload to Git accounts.
Github
- In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
- In the user settings sidebar, click SSH and GPG keys.
- Click New SSH key or Add SSH key.
- In the “Title” field, add a descriptive label for the new key. For example, if you’re using a personal Mac, you might call this key “Personal MacBook Air”.
- Paste your key into the “Key” field.
- Click Add SSH key.
AWS CodeCommit
- Go to the my security credentials page
- On this page, open AWS CodeCommit credentials tab
- Under the SSH Keys section click Upload SSH public key button.
- Paste your key into the “Key” field.
- Click Upload SSH public key.
Step 3 – Create Git Config File
Next, create a ssh configuration file for your user account. By default the user ssh configuration file exist under the .ssh directory in your home directory. Create and edit configuration file with the following file:
nano ~/.ssh/config
Append below entries to this file.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | Host github-proj1 HostName github.com User git IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_github_proj1 Host github-proj2 HostName github.com User git IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_github_proj2 Host aws-codecommit-proj3 Hostname git-codecommit.us-east-2.amazonaws.com User TECADMIN0123456789 IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_aws_codecommit_proj3 |
Save your file and close it. You have done with the required configuration of using multiple git accounts on a system.
Step 4 – Let’s Start Your Work
Your system is ready to use the multiple remote repositories from multiple accounts. You can connect your existing code with remote repository and push updates. For the new project, simply clone the repository on your machine and start your work.
You need to change host in git url as defined in ~/.ssh/config file. See the below examples:
For a New Repository
Repository from first Github account:
git clone ssh://github-proj1/user1/repo.git
Repository from second Github account:
git clone ssh://github-proj2/user2/repo.git
Repository from AWS CodeCommit account:
git clone ssh://aws-codecommit-proj3/v1/repos/myrepo
For an existing codebase
For the existing codebase, your can use the following commands to connect your code with remote repository. Then add and commit files to the repository.
cd my-codegit initgit remote add ssh://github-proj2/user2/repo.gitgit add .git commit -m "Initial commit"git push origin master
Conclusion
This tutorial helped you to configure multiple Git (Github, Gitlab, AWS Codecommit or Bitbucket etc) accounts on a single machine.