A loop statement is useful for executing iterative tasks. Using a loop a program can run a specific code block for multiple times as required.
In Java programming language, there are 3 types of loops used. In which for loop is one of the most used loop. Below is the list if loop available.
- for loop
- while loop
- do-while loop
Java – for Loop
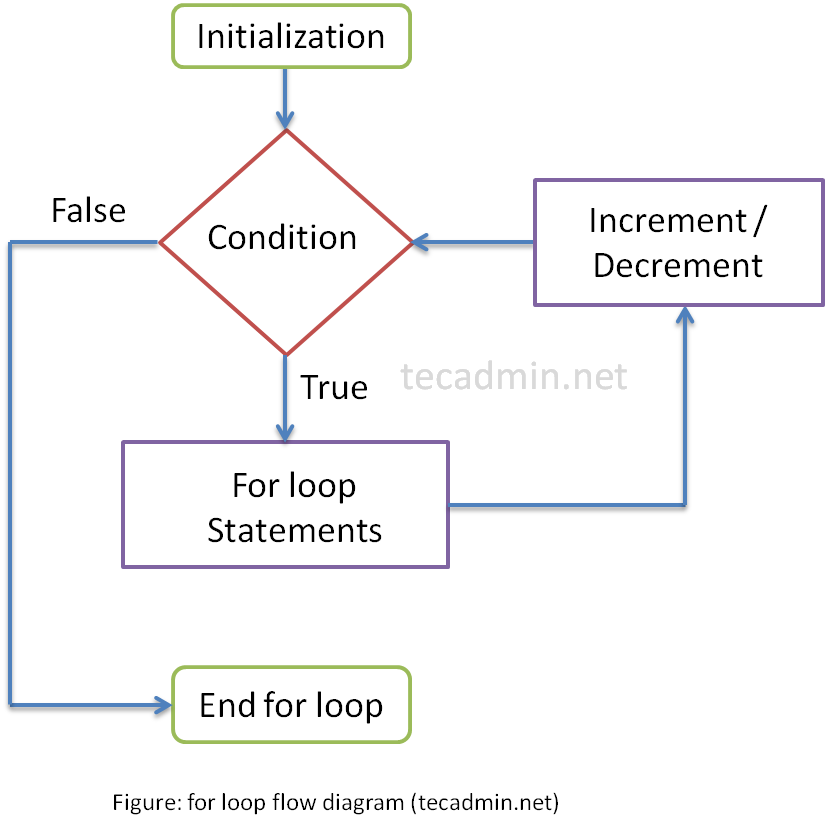
A for loop is the entry-restricted loop. Where a condition is checked before executing the code block.
If the condition evaluates to true, the block of code is executed and if the condition evaluates to false loop is terminated and control goes to just after the loop body.
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 | for (initialization; condition; increment/decrement) { // code block } |
for Loop Working
- Step 1 – Loop start with the initialization process (first time only).
- Step 2 – The conditions are checked. If the condition evaluates to false go to step 5. If the condition evaluates to true then continue to step 3.
- Step 3 – Code block is executed.
- Step 4 – Increment/Decrement Statement is executed and goto Step 2.
- Step 5 – Exit loop
for Loop Example
An example of for loop to print number 1 – 10.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | // C Program to calculate the sum of 1 to 100 numbers public class TestForLoop{ public static void main(String[] args) { // for loop run until i is less than or equal to 10 for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { System.out.println(i) } } |
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10