Docker Data Volumes
In docker, data volumes are useful for managing your data with Docker containers and host machines. Here you will find two way of managing data volumes on Docker containers.
- Using the data volume container.
- Using share data between the host and the Docker container
#1. Use Docker Data Volume Container
The Docker data volume container is same as other containers, but they just used for storage only. You can use storage of these containers to your containers. When you write data to your containers file system, it will be originally written to a storage container.
Create Data Volume Container:
$ docker create -v /data --name data_container centos
The above command will launch a container with name “data_container” having data volume at /data. The container will stop immediately due to no service. Now create your application container with –volumes-from flag.
Use Data Volume to New Container:
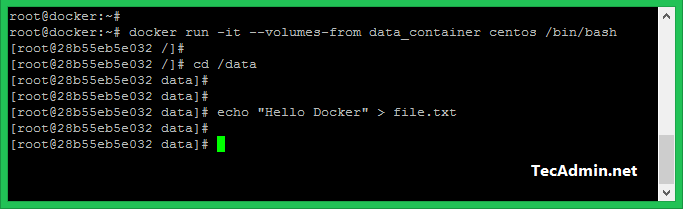
$ docker run -it --volumes-from data_container centos /bin/bash
This will provide you shell access to newly created container. Now use /data directory to create any number of files and directories on it.
[root@28b55eb5e032 /]# cd /data [root@28b55eb5e032 /]# echo "Hello Docker" > file.txt
Now you can exit from current instance. Also, you remote this using docker remove command. After that launch new instance using the same data volume and try to access the files created under /data directory.
Verify Files on Data Volume:
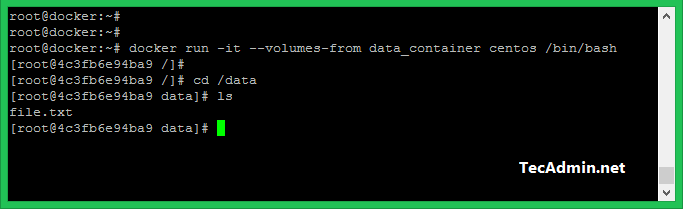
Let’s launch another container with the same data volumes and check available files on /data directory.
$ docker run -it --volumes-from data_container centos /bin/bash
#2. Sharing Host Volume to Docker Container
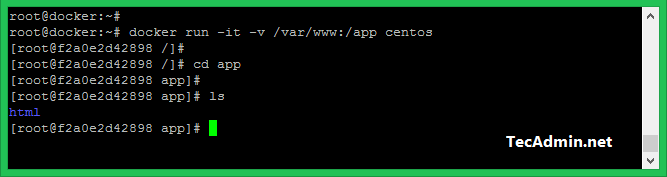
You can also share data between the host machine and docker container. For example you can share /var/www directory of host machine to /data directory. You can share any directory of the host machine to a container.
$ docker run -it -v /var/www:/data centos
Here /var/www is directory on host machine. Which is mounted on /data directory in Docker container.