A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is a common cyber-security threat that can have severe consequences if not properly addressed. In this type of attack, a malicious actor intercepts, relays, and potentially alters the communication between two parties who believe they are communicating directly with each other. This article will delve into the threats posed by MITM attacks, the techniques used by attackers, and the countermeasures that individuals and organizations can use to protect themselves.
Threats Posed by MITM Attacks
The most apparent threat posed by MITM attacks is the unauthorized access to sensitive information. By intercepting the communication between two parties, an attacker can steal data such as login credentials, personal identification information, financial data, and other sensitive material. The compromised data can then be used for various malicious activities, including identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage.
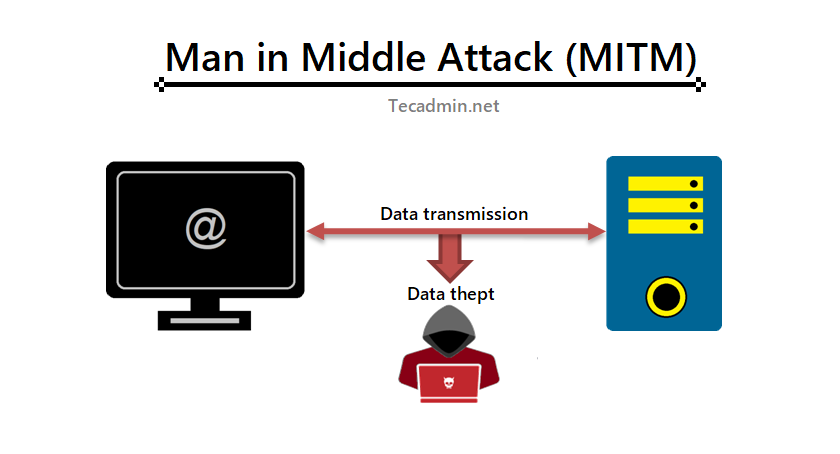
Moreover, in addition to stealing information, a MITM attacker can alter the communication between the two parties. This could include injecting malicious software into files being transferred, changing the content of a message, or redirecting a user to a malicious website. This capability makes MITM attacks a potent tool for spreading malware or disinformation.
Techniques Used in MITM Attacks
MITM attacks can be performed using a variety of techniques, each exploiting different vulnerabilities:
- IP Spoofing: The attacker masks their IP address to make it appear as if the data packets are coming from a trusted source.
- ARP Spoofing: The attacker sends falsified ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) messages to link their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate user on the network. This allows the attacker to intercept data meant for the legitimate user.
- DNS Spoofing: The attacker manipulates the domain name system (DNS) server so that it redirects internet traffic from legitimate sites to malicious ones controlled by the attacker.
- HTTPS Spoofing: The attacker sets up a website that looks identical to a legitimate one but operates under a slightly different URL. When a user accidentally enters this URL, they land on the attacker’s site, giving up their information without knowing they’re under attack.
- SSL Hijacking: The attacker intercepts the victim’s request to a secure (HTTPS) website and creates an unsecured connection with the server, while keeping a secure connection with the victim. The victim’s data then goes through the attacker before reaching the server, allowing the attacker to view or alter it.
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping: The attacker sets up a fake Wi-Fi access point (often known as an “evil twin”) and tricks users into connecting to it. Once a user is connected to the malicious Wi-Fi, the attacker can monitor their online activity.
Countermeasures Against MITM Attacks
Despite the potential risks posed by MITM attacks, there are numerous strategies and tools that can significantly mitigate these threats:
- Encryption: Implementing end-to-end encryption ensures that even if an attacker intercepts the communication, they will not be able to understand the content. Protocols such as HTTPS and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) can encrypt data transmitted over networks.
- VPNs: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a private network from a public internet connection, providing a secure tunnel for your data to pass through.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): PKI uses a pair of cryptographic keys (a public key and a private one) to encrypt and decrypt information. This ensures that even if an attacker intercepts the data, they cannot decipher it without the private key.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource, making it harder for an attacker to gain access to accounts.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping software and systems updated ensures that the latest security patches are installed, thereby reducing the potential vulnerabilities that an attacker can exploit.
- Secure Wi-Fi Practices: Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions. If it’s necessary to use public Wi-Fi, make sure to use a VPN.
- User Education: Ultimately, one of the most effective defenses against MITM and other cyber attacks is education. Users need to be aware of the risks and be able to recognize potential attacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while MITM attacks pose significant threats, understanding the techniques used by attackers and implementing appropriate countermeasures can provide robust protection. As technology continues to evolve, it’s important for cybersecurity measures to keep pace. Awareness, vigilance, and a proactive approach to security can go a long way in mitigating the risks of a Man-in-the-Middle attack.
