When it comes to safeguarding our important digital data, whether it’s personal photos, important business documents, or projects, having an effective backup strategy is essential. Among the myriad of backup approaches out there, the 3-2-1 backup strategy stands out as a popular and trusted method.
In this article, we will delve into the details of this strategy, explaining what it is, why it’s significant, and how to implement it.
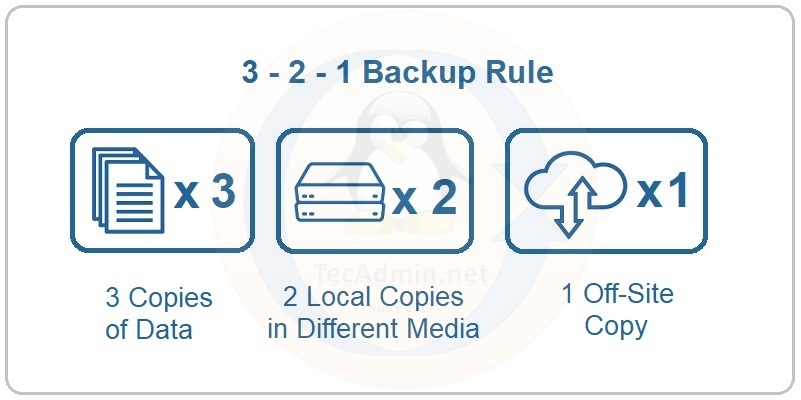
Defining the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a simple yet effective rule to ensure that your data remains safe and accessible. Here’s how it breaks down:
- 3 Total Copies of Data: Always have three complete copies of your data. This includes the original data plus two backup copies.
- 2 Of Which Are Local But On Different Mediums: Two of these copies should be stored on different devices or platforms. For instance, if you have data on your computer’s hard drive, one backup might be on an external drive, while another might be on a network-attached storage (NAS) device.
- 1 Copy Offsite: Always ensure that one of the three copies is stored offsite, away from the physical location of the other two. This could mean storing it in the cloud, on a remote server, or even on a hard drive kept in a different geographical location.
Why Is the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy So Important?
Several threats can compromise your data:
- Hardware Failures: Devices fail. Hard drives can become corrupt, or SSDs can wear out. By having multiple copies on different devices, you safeguard against the failure of one particular device.
- Software Problems: Software bugs, ransomware, or malware can corrupt your data. Having different versions backed up ensures you can roll back to a safer state.
- Natural Disasters: Events like fires, floods, or earthquakes can physically damage storage mediums. An offsite backup is essential in such cases.
- Human Error: Accidental deletion or overwriting of files happens. Multiple backups provide a safety net against such incidents.
How to Implement the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy
- Primary Data Copy: This is the data you use and access daily, usually stored on your computer’s hard drive or main storage device.
- First Backup (Local): Use an external hard drive, USB drive, or a NAS device. Regularly back up your primary data to this medium. Tools like Windows Backup (for Windows users) or Time Machine (for macOS users) can help automate this process.
- Second Backup (Also Local): Consider using a different method or medium than the first. If you used an external hard drive for the first backup, you might use a NAS or a different type of storage for this one. The idea is to diversify your backup formats.
- Offsite Backup: Cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, Backblaze, or Carbonite can be used. If you prefer physical offsite backups, regularly copy your data to a hard drive or another medium and store it in a different location, like a safety deposit box or a trusted family member’s house.
Regularly Test Your Backups
Having backups is great, but they’re of no use if they’re corrupt or not up-to-date. Periodically test your backups to ensure they’re functional. Try restoring some files to verify they work as expected.
Conclusion
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a fundamental principle in data management and protection. While the specifics of how you implement this strategy might differ based on your needs and available resources, the core tenet remains: diversify where and how you store your backups. In today’s digital age, where data loss can have significant repercussions, adhering to the 3-2-1 backup strategy offers peace of mind that your data is safe, come what may.