This is a most important topic for the security of the files and directories on your Unix/Linux systems. This tutorial covers the file permissions, how to check the current permissions on file and change it.
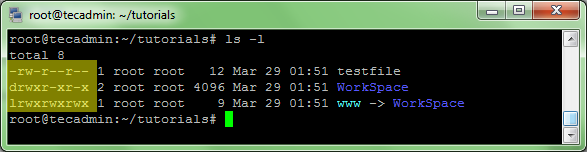
To identify the current permissions set on a file or directory. Run ls -l command on terminal. See below image, highlighted section shows the file type and permissions.
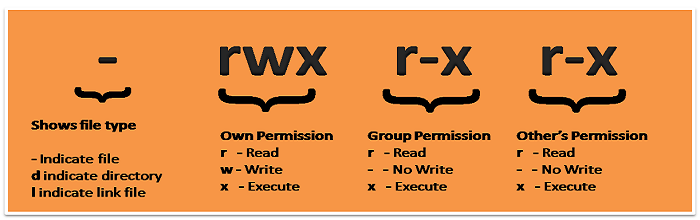
There are 10 bits defined with file permissions. Each has a special meaning. Below is the preview of file permissions defined for a file.
Every file on Linux has 3 types of members (owner, group, other) associated with them.
- The first bit shows the file type
- The 2, 3 and 4’th bit shows the permission of file owner
- The 5, 6 and 7’th bit shows the permission of group members
- The 8, 9 and 10’th bit shows the permission of other users
Type of Roles and Permissions
To understand file permission you must know about Roles and Permission types. There are three types of roles available in Linux systems (User, Group, and Others). Each role has 3 types of permissions (Read, Write, and Execute).
Roles:
- User (Owner)
- Group (All group members)
- Other (All other users
Permissions:
- Read (r) – Member can read the file content or List files in a directory
- Write (w) – Member can write content to file or Create, list, rename, delete file in a directory
- Execute (x) –< Member can execute any file like sheel script or enter to the directory, and access files and directories
Ways to Change File Permissions in Linux
The chmod command allows users two ways to set permission on any file. Read below about both options:
Symbolic Notation
The symbolic notation used to set permission with alphabets as follwoing:
Roles:
- u – User
- g – Group
- o – Other
Permissions:
- r – read permission
- w – write permission
- x – execute permission
Octal Notation
The octal notation allows users to set permission in number formats. Each permission have the pre-defined number as following
- Read (r) – 4
- Write (w) – 2
- Execute (x) – 1
Possible combinations as as follows:
7 - 4+2+1 (rwx) (Read + Write + Execute) 6 - 4+2 (rw-) (Read + Write) 5 - 4+1 (r-x) (Read + Execute) 4 - 4 (r--) (Read) 3 - 2+1 (-wx) (Write + Execute) 2 - 2 (-w-) (Write) 1 - 1 (--x) (Execute) 0 - 0 (---) (None)