What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is a technical specification for email authentication that was developed jointly by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and DMARC.org. DMARC allows email senders to create DMARC records in DNS that tell receivers what to do if the email being sent doesn’t pass either SPF or DKIM authentication checks.
In this blog post, we will show you how to create DMARC records for your domain using DMARC.org’s free DMARC reporting tool.
How to Create DMARC Record for Your Domain
A DMARC record is a type of TXT record that helps to prevent email spoofing.
To generate a DMARC record for your domain, you will need to create a TXT record on DNS with the following values:
_dmarc.example.com TXT "v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected]; fo=1;"
Details about the above record:
_dmarc.example.com– Is the DNS record name, where example.com is your domain name.TXT– Is the DNS record typev=DMARC1indicates that this is a DMARC record.p=none– specifies that no action to be taken if DMARC validation failed.p=none: Monitors your email traffic. No further actions are taken.p=quarantine: Sends unauthorized emails to the spam folder.p=reject: The final policy and the ultimate goal of implementing DMARC. This policy ensures that unauthorized email doesn’t get delivered at all.
rua=mailto:[email protected]is an email address to send daily reports.fo=1, says that all failures should be reported.
You can also use some more options with the DMARC record as described below:
ruf=mailto:[email protected]specify where DMARC forensic reports should be sent.pct=50says that the 50% of emails will be DMARC verified. By default is all emails is verified
Why do you need DMARC for Email
DMARC is an important security protocol that helps to protect email users from spam and phishing attacks. By authenticating the sender of an email, DMARC helps to ensure that only messages from legitimate sources are delivered to inboxes.
Additionally, DMARC provides a mechanism for reporting suspicious activity, allowing organizations to quickly identify and respond to potential threats. As email continues to be a primary means of communication for businesses and consumers alike, DMARC provides an essential layer of protection against the ever-growing number of cyber-attacks.
How does the DMARC Work?
DMARC is an acronym for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. It is an email authentication protocol that builds on the existing SPF and DKIM protocols to help ensure that only legitimate emails are delivered to your inbox.
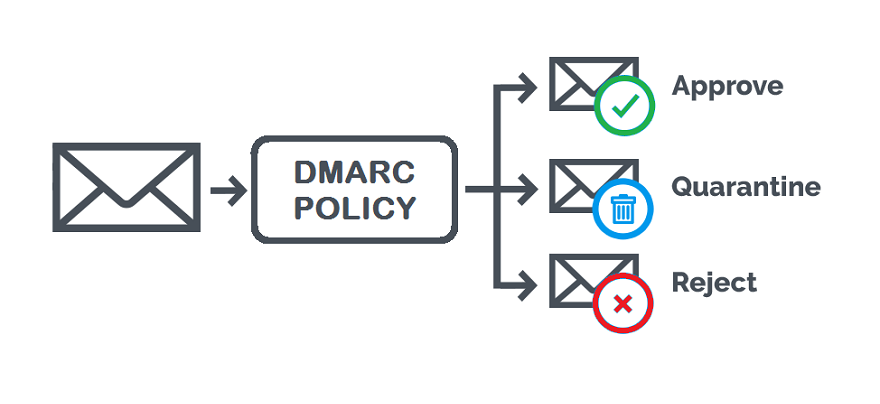
DMARC works by verifying that the domain in the “From” field of an email matches the domain of the email server that sent the message. If the domains don’t match, then the email is considered to be fraudulent and is not delivered.
DMARC also provides a mechanism for reporting on emails that fail authentication, so that senders can be notified and take action to correct the problem. Ultimately, DMARC helps to protect both email users and email providers from spam, phishing, and other forms of fraud.
