The “Connection Refused” error means that the computer is not accepting connection requests to the requested IP address and port. Connection requests may be blocked by a firewall, which is why “Connection refused” is displayed.
When a computer receives a connection request from an IP address and port that it wants to connect to, but the firewall blocks the connection, the “Connection Refused” error message appears. “Connection refused” can be due to a firewall blocking connection requests. In some cases, none of the services are listening on the requested port also causes the “Connection Refused” error.
The Problem:
Today, I installed a new Ubuntu system on my LAN network. I faced an error “Port 22: Connection refused” during the SSH connection to this system. After a bit troubleshoot, I got that there is no SSH server running on the newly installed system.
I got the error message below:
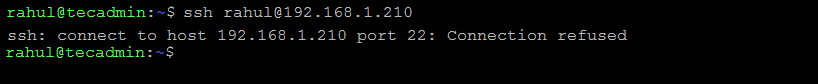
How to Resolve “Port 22: Connection refused” Error
There are the 4 most common reasons behind this error. One or more reasons can cause this issue as listed blow.
- SSH Server is not installed
- SSH service is not active
- SSH service is running on a different port
- SSH port is blocked by the firewall
Let’s discuss all the possible solutions one by one.
1. SSH Server is not installed
The OpenSSH is used for SSH service on Debian-based systems. Some of the newly installed systems may not have SSH daemon. Most likely, when you install a new Desktop system, the OpenSSH packages are not included by default.
You can run the following commands to install the ssh service on your system.
sudo apt udpate && sudo apt install openssh-server
Once the installation is finished, you can connect to your system on port 22. If you are still facing issues, check for other reasons defined below.
2. Check SSH Service is Active and Running
Generally, the SSH service is started automatically after the installation. But might be service is stopped due to some reason. To check the current status of the SSH service, execute:
sudo systemctl status ssh
If the SSH service is not running or not active, use the below-mentioned commands to enable service on system startup and start service.
sudo systemctl enable sshsudo systemctl start ssh
Once the service is started successfully, you can connect to your system over ssh. In case, you still face the same error, check for the next possible issue.
3. SSH service is running on a different port
Might be the SSH service is listening on a different port. That is also a best practice for securing servers. You can find out the SSH server port by running the following command.
ss -tulpn | grep ssh
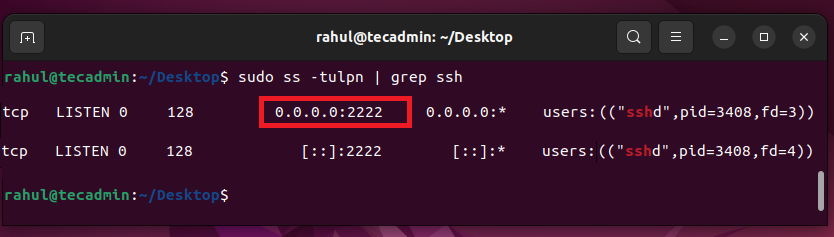
The above screenshot shows that the SSH service is listening on port 2222. You should connect the remote system with SSH on port 22. We can define a port number with an SSH connection as the below-mentioned command.
ssh -p 2222 [email protected]
Hope this will resolve your issue. If still you are facing the same issue, check the below suggestion.
4. SSH port is blocked by the firewall
This is the most common cause that the firewall is blocking the requests.
Now, you need to identify, what firewall are you using. If the remote system is on the cloud hosting, check the security group of that hosting.
On the systems with physical access, can check if UFW or Firewalld is active.
- Using UFW
Check the status of the UFW firewall with the below command:
sudo ufw statusIf the firewall is in an active state, you can open Port 22 with the below-mentioned command.
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp - Using FirewallD
Check if the firewalld daemon is active and running:
sudo systemctl status firewalldIf the output shows
Active: active (running), then you can open the SSH port by running the following command.sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=22/tcpThen reload the firewall to apply changes.
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Conclusion
In this blog post, we talked about four possible reasons for the error “Port 22: Connection refused” and gave solutions for each one. We hope this helps you fix the problem.
If you know of any other reasons for this issue, please share them in the comments.


2 Comments
You sure about this section?
If the output shows Active: active (running), then you can open the SSH port by running the following command.
sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –zone=public –add-port=80/tcp
SSH on port 80?
Thanks for pointing it. Fixed typo.