Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol used to remotely log into a Linux system and execute commands on it. It provides a secure encrypted connection between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. System administrators often use SSH to remotely manage servers.
Displaying a warning message to unauthorized SSH access is an important step in securing your Linux system. A warning message can inform users of security policies, warn them of the consequences of unauthorized access, and provide important information about the system they are accessing. In this article, we will guide you through the process of setting a custom SSH warning message in Linux.
Step 1: Create the SSH Banner File
To display a warning message, you will first need to create a file that contains the message text. The banner file is usually located in the /etc/ssh directory and is named banner. To create this file, use the following command:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/banner
This will open the nano text editor, where you can write the custom warning message.
For example, I am using the following message:
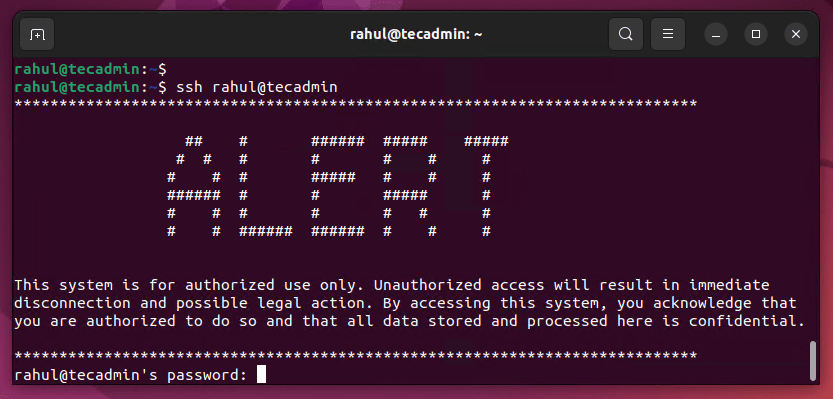
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | ************************************************************************************* ## # ###### ##### ##### # # # # # # # # # # ##### # # # ###### # # ##### # # # # # # # # # # ###### ###### # # # This system is for authorized use only. Unauthorized access will result in immediate disconnection and possible legal action. By accessing this system, you acknowledge that you are authorized to do so and that all data stored and processed here is confidential. ************************************************************************************* |
Save the file and close it.
Step 2: Configure the SSH Daemon
Once the banner file has been created, you need to configure the SSH daemon to display the banner when a user logs into the system using SSH. To do this, you will need to edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. To edit this file, use the following command:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Find the line that starts with “Banner” and uncomment it by removing the # symbol in front of it. Then, add the path to the banner file you created in Step 1:
1 | Banner /etc/ssh/banner |
Save the file and close it.
Step 3: Restart the SSH Daemon
Once the banner file has been created and the SSH daemon has been configured, you need to restart the SSH daemon to apply the changes. To restart the SSH daemon, use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Step 4: Verify the Warning Message
To verify that the custom warning message is being displayed, you can use an SSH client to connect to the Linux system. When you log in, you should see the warning message displayed before the login prompt.
Conclusion
In conclusion, displaying a warning message for unauthorized SSH access is an important step in securing your Linux system. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily set a custom SSH warning message in Linux. This will help ensure that users are aware of security policies and the consequences of unauthorized access before logging into the system.
