Ever looked at your phone or computer storage and wondered what all those letters—MB, Mb, MiB—really mean? You’re not alone! These terms pop up everywhere, whether you’re downloading a file, checking your internet speed, or buying a new hard drive. But here’s the thing: they’re not all the same, even though they sound similar. Mixing them up can leave you confused about how much space or speed you’re actually getting, and nobody wants that headache.
So, let’s clear the air. In this article, I’ll break down the difference between MB (megabyte), Mb (megabit), and MiB (mebibyte) in a way that’s easy to follow—like we’re just chatting about it. By the end, you’ll know exactly what each one means, why they matter, and how to spot them in the real world. Ready to sort out this digital puzzle? Let’s jump in!
Understanding the Basics: Bits and Bytes
To fully grasp the differences between MB, Mb, and MiB, one must first understand the fundamental units of digital information – bits and bytes.
A bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a single binary value of either 0 or 1. In contrast, a byte is a group of eight bits, which can represent a single character, such as a letter or number.
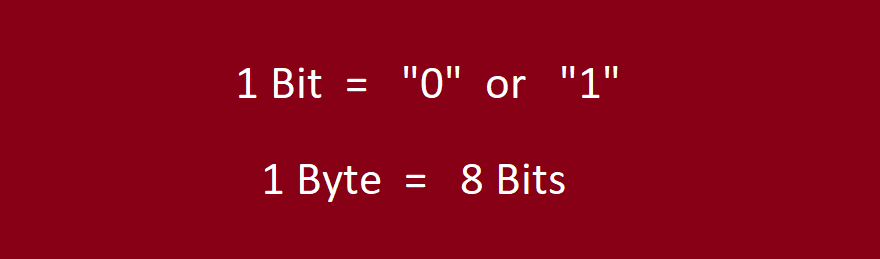
Megabytes (MB) – A Common Unit of Digital Storage
A Megabyte (MB) is a widely-used unit of digital storage, often used to express the size of files or storage capacities of devices. One Megabyte is equal to 1,000,000 bytes or 8,000,000 bits. The prefix ‘Mega’ signifies one million, indicating the magnitude of this unit.
Example use case: A 16MB image file would be large enough to store a high-quality photograph taken by a digital camera.
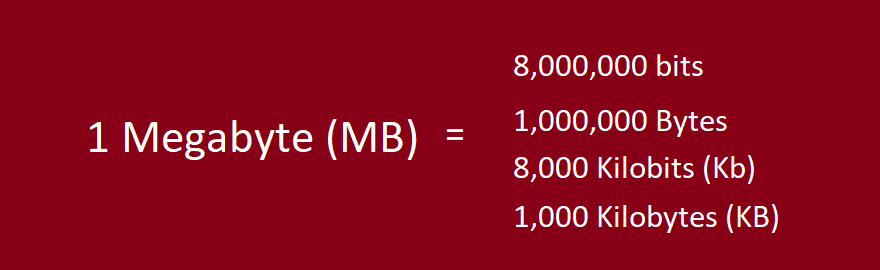
Megabits (Mb) – A Unit for Data Transmission Rates
A Megabit (Mb) is another common digital unit, predominantly used to measure data transmission rates, such as internet connection speeds. One Megabit is equal to 1,000,000 bits or 125,000 bytes. It is crucial to note that the term ‘Megabit’ refers to bits, not bytes.
Example use case: A 100 Mb/s internet connection would allow you to download data at a rate of 100 Megabits per second.
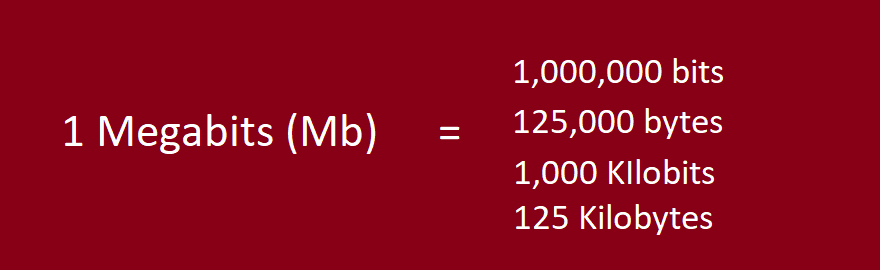
Mebibytes (MiB) – A Unit Based on Binary Prefixes
A Mebibyte (MiB) is a digital storage unit based on binary prefixes. It is primarily used in computer science and programming to provide a more precise representation of digital storage. One Mebibyte is equal to 1,048,576 bytes or 8,388,608 bits. The prefix ‘Mebi’ stands for “Mega Binary,” representing the binary nature of this unit (2^20).
Example use case: A 64 MiB computer memory module would have a storage capacity of approximately 67,108,864 bytes.
Distinguishing Between the Units
Understanding the differences between MB, Mb, and MiB is crucial to avoid confusion and potential errors in various digital contexts. Here are some key points to remember:
- MB and MiB both represent digital storage units, whereas Mb refers to data transmission rates.
- MB is based on decimal prefixes (1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes), while MiB uses binary prefixes (1 MiB = 1,048,576 bytes).
- To convert between Megabytes and Mebibytes, one can use the conversion factor of 1 MB ≈ 0.9537 MiB.
Conclusion
And there you have it—the mystery of MB, Mb, and MiB unraveled! It’s pretty cool how these little units shape the way we understand data, whether it’s how fast your internet is or how much stuff you can store on your device. Knowing the difference means you won’t get tripped up next time you’re comparing internet plans or figuring out if a file will fit on your USB drive. It’s like having a secret decoder ring for the digital world.
So, next time you see those letters, you’ll be the one nodding knowingly instead of scratching your head. Tech doesn’t have to be confusing, and now you’ve got this one sorted. Go ahead and impress your friends with your newfound knowledge—I won’t tell them you had a little help figuring it out!
