If you’re a Linux user, and you use distros such as Ubuntu or Debian, then you will have surely seen the command apt update. But what is it, exactly, and why do you want to run it often? In this article, we are going to break down the apt update command into simple words and explain what role it has in keeping your system running as it should.
What is apt?
APT is an acronym for Advanced Package Tool, and it is a command-line utility that allows us to handle software packages in Debian-based Linux distributions such as Ubuntu. An example of a package manager that you can use is called apt and is used to install, upgrade, and remove packages on your system.
What does the apt update Command Do?
This is where the apt update command comes in, as it communicates with the software repositories (servers that will host the software packages). It updates your local database with this information so your system is aware of which packages are out of date or need to be updated.
Here’s the simplest way to explain what happens when you use apt update:
- Checking Repositories: The system will connect to repositories mentioned in its configuration files (files found at
/etc/apt/sources.listand/etc/apt/sources.list.d/). - Downloading Package Information: It fetches updated information about all available software packages from these repositories, including the new version of the packages along with their requirements and any updates or patches.
- Updating the Local Cache: It updates the cache of available packages by downloading it to your computer. This cache is what apt uses when you are attempting to install or upgrade software.
Just to be clear, apt update does not install or upgrade any software; it merely updates the list of available packages and their versions.
Why is apt update Important?
Having understood what apt update does, let us now find out why running this command regularly is important:
- Keeping Your System Up-to-Date: It ensures the software developers release of updates to fix bugs, patch security vulnerabilities, and improve performance. The act of this refresh is simply ensuring that when you may eventually wish to install or upgrade some piece of software, you are getting the latest version, which could potentially contain critical fixes.
- Security: Execute apt update to make sure your system can gain access to new security bug patches. Without having knowledge of what packages are available to upgrade, you can miss vital security updates (which you miss as package upgrades), rendering your system open to exploits.
- Prevents Package Errors: Without this update, you can get errors installing or upgrading software because your machine tries to pull an old or wrong version of software packages. This would not happen if you did regular updates because your local cache would always be correct.
- Quickly Ensured Installation: With apt update making sure that your system is aware of the latest software versions, any installations following this command will be both speedier and more reliable.
When to use apt update Command?
Because apt is a low-level tool, it does not necessarily need to be run before every single operation. Normally apt update is used on a daily basis for keeping the system up to date. Below are some example scenarios when you should run the command:
- Before Upgrading Packages: If you wish to upgrade your currently installed software, using apt update makes sure that you are upgrading to the most recent available versions.
- After Adding New Repositories: If you’ve added new software sources to your system (for instance, a third-party repository), you ought to run apt update for your system to be conscious of the new packages.
- After a Fresh Installation of System: If you install a fresh copy of Ubuntu or Debian, the first step is to run apt update to allow the system updates.
How to Run apt update?
Issuing the apt update command is trivial. Launch a terminal window, and input this command:
sudo apt update
This command requires administrative privileges, so it’s being executed with sudo.
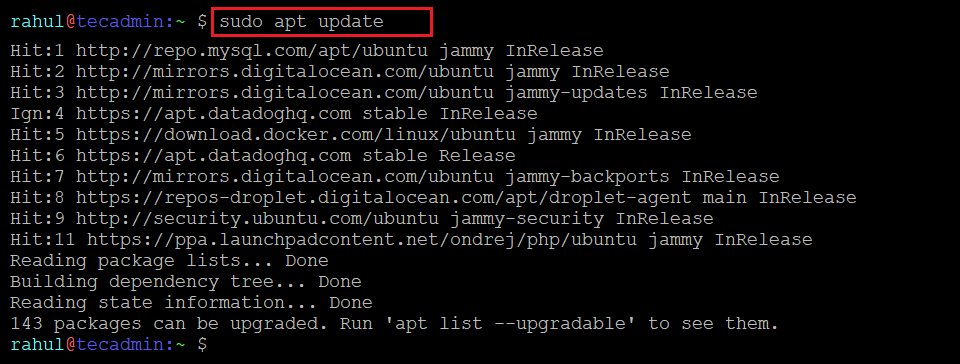
It would ask you for your password. Type it in this next step. After you run the command, you’ll see a table including a list of repositories that were checked and the number of available updates. You can then install or upgrade software, as needed.
Conclusion
As a user of a Debian-based Linux distribution, the apt update command is one of the important utilities you will come across. This will ensure, for example, that your system is aware of the latest software versions, security patches, and updates. You should run this command periodically for ensuring your system is secure, stable, and smoothly running as it allows your system to clean itself.


