With the exponential growth of data, managing storage and analyzing disk usage has become an essential task for system administrators and everyday computer users alike. Understanding how your disk space is being utilized helps you optimize your system and make informed decisions about storage allocation. DUF, or Disk Usage/Free Utility, is a powerful, cross-platform tool designed to help you do just that. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to DUF and how it can be used on Linux, BSD, macOS, and Windows systems.
1. What is DUF?
DUF is an open-source, user-friendly, and highly customizable command-line tool for monitoring and analyzing disk usage on various operating systems. It is written in Go and provides detailed information about disk usage, free space, and filesystems in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format. DUF supports Linux, BSD, macOS, and Windows, making it a versatile solution for users across platforms.
2. Installing DUF
To get started with DUF, follow the installation steps for your respective operating system:
- Ubuntu and Other Debian-based systems:
https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.8.1/duf_0.8.1_linux_amd64.debsudo apt install -f ./duf_0.8.1_linux_amd64.deb - On Fedora and Other RHEL-based systems:
https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.8.1/duf_0.8.1_linux_amd64.rpmrpm -ivh duf_0.8.1_linux_amd64.rpm - On Arch Linux:
pacman -S duf - On FreeBSD:
pkg install duf - On macOS:
brew install duf
3. Using DUF
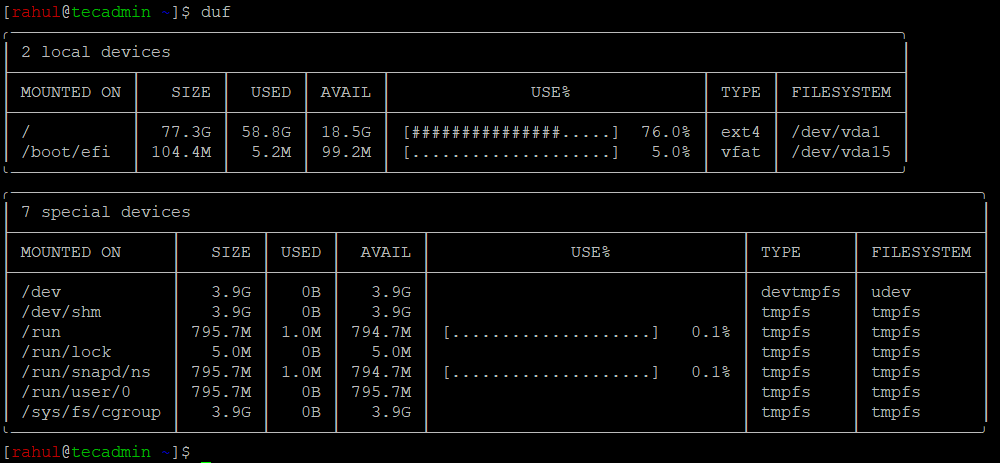
After installing DUF, open a terminal or command prompt, and simply type `duf`. This will generate a table showing an overview of your mounted filesystems, their total size, used space, available space, and usage percentage. The output will also include information about the mount points and the filesystem type.
4. Customizing DUF Output
DUF offers various options for customizing the output to suit your needs:
- To show only specific filesystems, use the
--only-fsflag, followed by a comma-separated list of filesystem types. For example:duf --only ext4 - To hide specific filesystems, use the
--hide-fsflag, followed by a comma-separated list of filesystem types. For example: .duf --hide-fs tmpfs,overlay - To display the output in a of the specific coloumn, use the –output flag. For example:
duf --output mountpoint,avail,filesystem - To sort the output based on a specific column, use the
--sortflag, followed by the column name. For example:duf --sort size
DUF in Action
DUF can be utilized in various scenarios, such as:
- Identifying large files or directories consuming significant disk space
- Monitoring disk usage on remote servers using SSH
- Comparing disk usage across different filesystems or storage devices
Conclusion
DUF is a powerful and flexible utility that simplifies disk usage monitoring and analysis for users on Linux, BSD, macOS, and Windows. With its visually appealing output and numerous customization options, DUF helps users understand their disk space allocation and make informed decisions about storage management. By integrating DUF into your daily workflow, you can ensure optimal use of your storage resources and maintain a healthy and efficient system.

