SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a secure file protocol used to access, manage, and transfer files over an encrypted SSH transport session. Security first is an thumb rules for the system administrators. Some times you may need to provide FTP/SFTP access to development or other teams to access file on remote server. This will allow you a secure channel to provide limited access to specific files and directories.
This tutorial will help you to create SFTP only user (without ssh shell access) on Ubuntu systems. And restrict (chroot) the SFT user account to specific directory only. Also disable the shell access to user.
Prerequisites
- A running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system
- You must have sudo privileged account with shell access
Step 1 – Create User
First of all, create a user account in your system to use as sftp user. The following command will create a new account named sftpuser with no shell access. You can change the username of your choice
sudo adduser --shell /bin/false sftpuser
Step 2 – Create Directory for SFTP
Now, create the directory structure to be accessible by the sftp user.
sudo mkdir -p /var/sftp/files
Here we will allow user to access “files” directory only.
Now, change the ownership of the files directory to the sftpuser. So that sftpuser can read and write on this directory only.
sudo chown sftpuser:sftpuser /var/sftp/files
And set the owner and group owner of the /var/sftp to root. The root user has read/write access on this access. Group member and other account have only read and execute permissions.
sudo chown root:root /var/sftpsudo chmod 755 /var/sftp
Step 3 – Configure sshd for SFTP Only
Now edit the SSH configuration file in a text editor
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
and add the following settings at end of file.
Match User sftpuser ForceCommand internal-sftp PasswordAuthentication yes ChrootDirectory /var/sftp PermitTunnel no AllowAgentForwarding no AllowTcpForwarding no X11Forwarding no
Save the configuration and restart SSH service to apply changes.
sudo systemctl restart ssh
All done, SFTP only use is successfully created on your Ubuntu system. Now try logging into the remote system with the new user’s credentials, and check if everything is working correctly.
Step 4 – Connect to SFTP User
Once can connect to remote SFTP server using command line or graphical applications like Filezilla or WinSCP. In this tutorial, I will show you both ways to connect sftp only account on Ubuntu system.
Linux users can use sftp command line utility to connect to remote sftp instance.
sftp [email protected]
[email protected]'s password:
sftp>
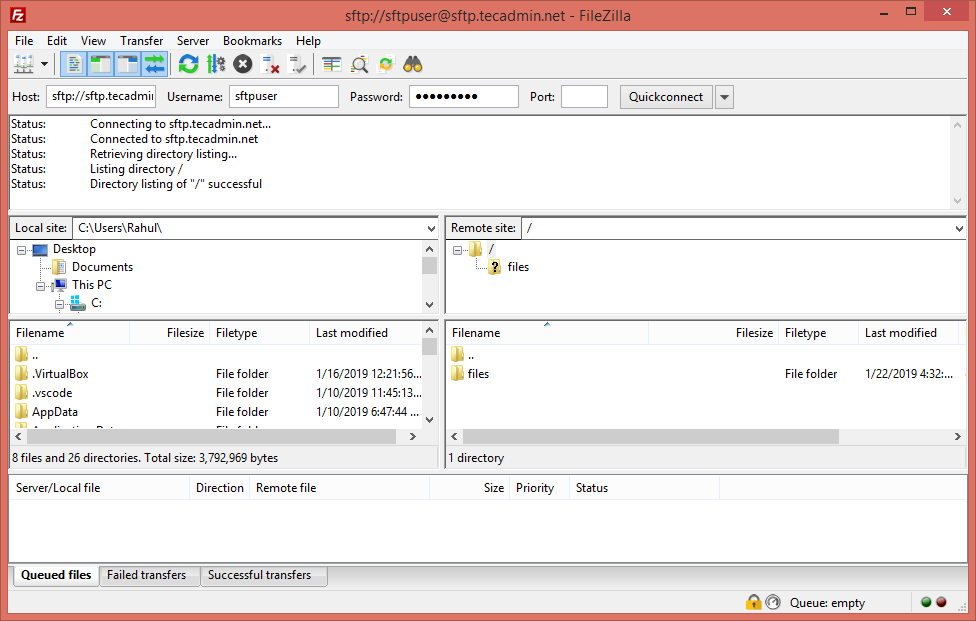
GUI interface or Windows users can use graphical sftp clients. For example, use filezilla client to connect remote sftp only account on remote system.
Verify no shell access:
As this account is configured for SFTP only connection. So if any user tried to connect via SSH will be disconnected immediately after successful authentication. User will get below message:
ssh [email protected]
[email protected]'s password:
This service allows sftp connections only.
Connection to sftp.tecadmin.net closed.
Conclusion
This tutorial describes you to create a sftp only user account on Ubuntu system. Disabled shell access for the same account to restrict user to sftp access only.


2 Comments
I think there is a typo in:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
To restart the SSH daemon (sshd) should this be:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
?
Hi Golfman,
The daemon name is “ssh” in Debian-based systems, and Redhat-based systems use “sshd”.