Nagios Core formally known as Nagios is an open source infrastructure monitoring system. The Nagios application periodically checks on critical parameters of the application, server and network resources. For example, Nagios server can monitor CPU load, disk space, memory usage, the number of currently running processes on a remote server. Also sends warning, critical or recovery notifications to the responsible persons over email, sms etc.
Nagios core is freely freely available from the official sites to deploy on your servers. In this tutorial, we will describe you the steps to install and configure Nagios server on a Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system.
Step 1 – Installing Apache
Apache is the popular web server required to serve Nagios web pages. The following commands will help you to install or upgrade Apache web server on your Ubuntu system.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install apache2
Nagios configuration required two Apache modules od_authz_groupfile and mod_auth_digest, which is not enabled by default. Execute the following command to enable reqiored modules.
sudo a2enmod authz_groupfile auth_digest
Here mod_authz_groupfile extends the authorization types with group and group-file. And auth_digest is used for user authentication using MD5 Digest Authentication.
Step 2 – Installing Nagios on Ubuntu 20.04
Nagios 4 stable version is available in the default Ubuntu software repositories. At the time of writing, Nagios version 4.3.4 available for Ubuntu 20.04 systems.
Run the following commands as sudo privileged account to install Nagios on Ubuntu system.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install nagios4 nagios-nrpe-plugin nagios-plugins-contrib
The command above will install a bunch of packages, including Nagios Core, Nagios Plugins, and Apache.
Step 3 – Configure Nagios Authentication
Next follow the below instructions to configure Apache and Nagios authorization.
Create nagiosadmin User – Create a Nagios user with name “nagiosadmin” to grant administrative privileges. Make sure to keep username as it is. Use htdigest command to create a new user:
sudo htdigest -c /etc/nagios4/htdigest.users Nagios4 nagiosadmin
Enter password and confirm password:
Adding password for nagiosadmin in realm Nagios4. New password: Re-type new password:
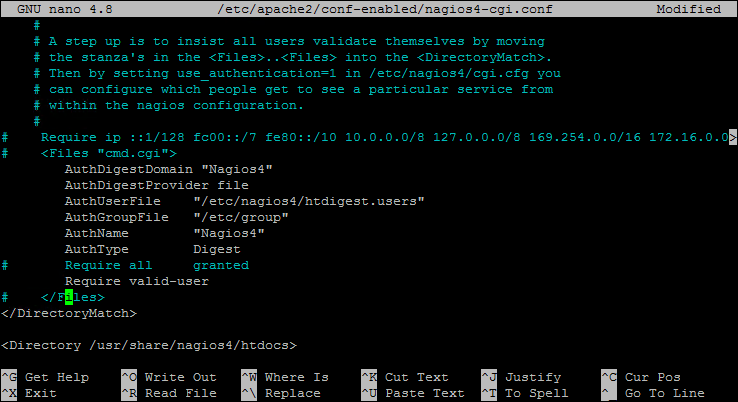
Configure Apache – Edit Nagios4 Apache configuration file and comment / un-comment few lines describes below. This will allow Nagios server to access from public network.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/nagios4-cgi.conf
- Comment Require IP line
- Files start and closing tag only
- Comment “Required all granted”
- Uncomment “Require valid-user”
Configure Nagios4 CGI Authentication – Next edit the /etc/nagios4/cgi.cfg configuration file and set use_authentication to 1. This option controls whether or not the CGIs will use any authentication when displaying host and service information, as well as committing commands to Nagios for processing.
sudo nano /etc/nagios4/cgi.cfg
use_authentication=1
Once you make all necessary changes, apply them by restarting the Apache and Nagios4 services.
sudo systemctl restart apache2sudo systemctl restart nagios4
That’s it. You have completed all the required settings.
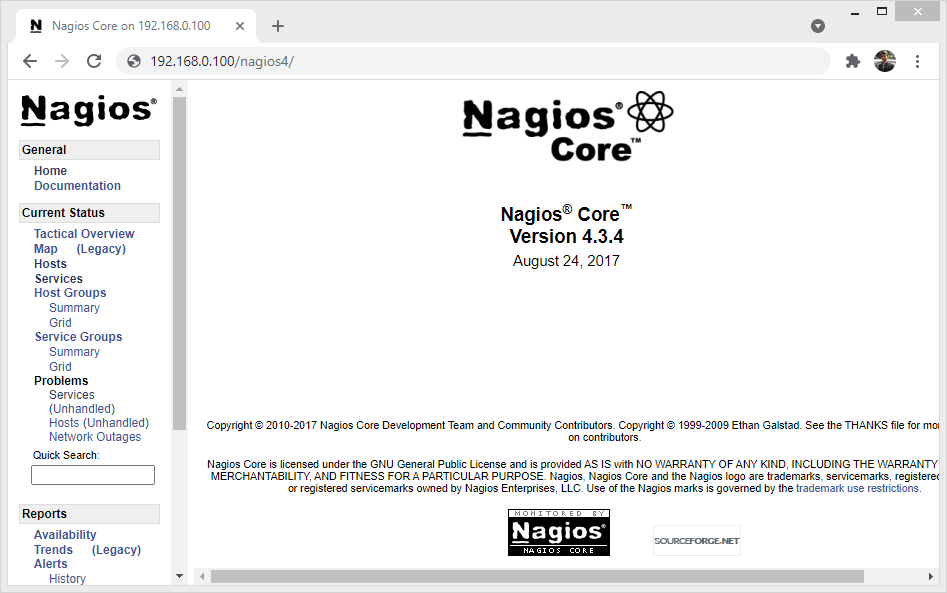
Step 4 – Access Nagios Web Interface
You can access nagios web interface using the server IP address or domain pointed to that server. The installer creates a Apache configuration file for nagios. You can access Nagios at a sub url as “/nagios4”.
http://server_domain_or_ip/nagios4
You will be prompted to inter username and password. Enter the “nagiosadmin” user credentials to access Nagios web page.
Conclusion
This tutorial helped you to install Nagios server on Ubuntu systems. Follow our next tutorial to add host to monitor through Nagios server.