If you manage a network with more than a few devices, you need monitoring software to keep tabs on all of them. Nagios is a leading open-source monitoring solution that alerts you when something goes wrong and gives detailed information when something needs your attention. This article covers how to monitor remote Linux hosts with Nagios. If you don’t have much experience with network monitoring or systems administration, you may find some of the jargon in this article difficult to understand. But don’t worry—we’ll explain everything that you need to know about monitoring software, remote hosts, and Linux servers. By the end of this article, you’ll be ready to begin monitoring your own network using Nagios.
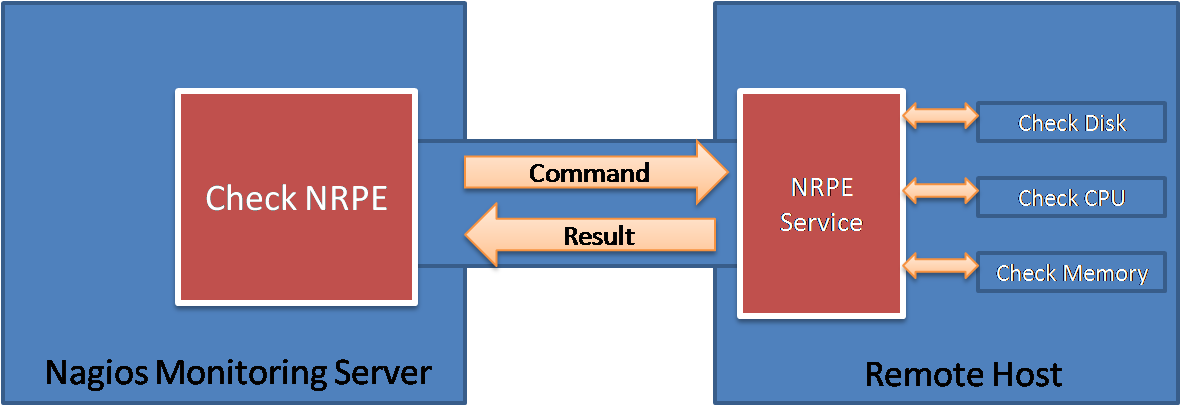
This article will help you to install NRPE service on your Linux system and add a host in the Nagios server for monitoring.
What is NRPE?
Nagios Remote Plugin Execution (NRPE) is an open-source monitoring plugin that allows you to monitor remote Linux hosts from a Nagios server. It uses TCP port 5666, which is normally not open on a firewall. If a firewall is blocking this port, you can install the Nagios NRPE proxy on the Nagios server and configure the firewall to allow TCP port 5666 from the IP address of the proxy server. NRPE is much more efficient than authentication methods like SSH and Telnet, which are more resource-intensive and require the Nagios server to have a user account on each remote host. With NRPE, Nagios authenticates with the user accounts on the remote host and uses the account’s permissions to access the remote host’s system information.
Step 1 – Configure NRPE on Linux Host
Follow the below steps to install and configure NRPE on the client machine and check connectivity with the Nagios server.
A. Installing NRPE Client
First, you need to install the remote plugin on each remote host that you want to monitor with Nagios. Open a terminal window on each remote host, and type the following to install the Nagios remote plugin on the host.
- On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
sudo dnf install nrpe nagios-plugins* - On Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nagios-nrpe-server nagios-plugins
B. Configure NRPE
After successfully installing the NRPE service, Edit the NRPE configuration file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg in your favorite editor and add your Nagios service IP in allowed hosts.
vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1, 192.168.1.100
Where 192.168.1.100 is your Nagios server ip address.
After making the above changes in nrpe configuration file, Lets restart NRPE service as per your system
sudo service nrpe restart# On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora sudo /etc/init.d/nagios-nrpe-server restart# On Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint
C. Verify Connectivity from Nagios
Once you’ve finished configuring Nagios to monitor remote Linux hosts, test the connection. Open a new terminal window, and type the following commands on the Nagios server. Here 192.168.1.11 is the remote host system IP address.
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.11
NRPE v2.15
Step 2 – Add Linux Host in Nagios
We recommend using the NagiosQL3 web interface for managing the configuration of the Nagios server. The below steps is for CLI lovers. To add a host to your Nagios server from the command line.
First, create a configuration file
sudo vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/MyLinuxHost001.cfg
#########################################################
# Linux Host 001 configuration file
#########################################################
define host {
use linux-server
host_name Linux_Host_001
alias Linux Host 001
address 192.168.1.11
register 1
}
define service{
host_name Linux_Host_001
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
max_check_attempts 2
check_interval 2
retry_interval 2
check_period 24x7
check_freshness 1
contact_groups admins
notification_interval 2
notification_period 24x7
notifications_enabled 1
register 1
}
#########################################################
# END OF FILE
#########################################################
Now verify configuration files using the following command. If there are no errors found in the configuration, restart the Nagios service.
nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfgservice nagios restart
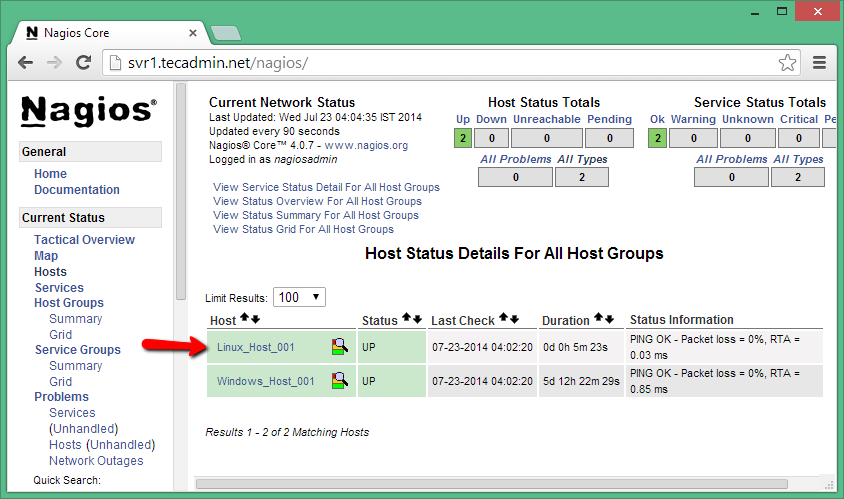
Step 3 – Check Host in Nagios Web Interface
Open your Nagios web interface and check for new Linux hosts added to Nagios core service. In my case, it looks like the below.
Conclusion
If you manage a network with more than a few devices, you need monitoring software to keep tabs on all of them. Nagios is a leading open-source monitoring solution that alerts you when something goes wrong and gives detailed information when something needs your attention. If you don’t have much experience with network monitoring or systems administration, you may find some of the jargon in this article difficult to understand. But don’t worry – we’ll explain everything that you need to know about monitoring software, remote hosts, and Linux servers. By the end of this article, you’ll be ready to begin monitoring your own network using Nagios. Ready to get started? Now that you know what NRPE is and how it works, you can install the corresponding software on your remote hosts and Nagios server. Then, you can start monitoring your network with Nagios to keep tabs on all of your devices.

11 Comments
is it possible if nrpe pkg vary both end remote host and nagios server.
HI Rahul,
i need realtime examples for how to monitor the servers and services in nagios.
HI Rahul,
i have added hosts in my nagios config but has not configured nrpe in any remote hosts…although i can c the hosts added in my nagios server but nagios not showing it correctly. Even when my hosts is down it is showing as up…is this the reason that i have not configured nrpe in my remote host?? please reply at the earliest.
Hi Prateek,
check_ping does not require nrpe on the remote system. Check ping will return OK only if remote system IP ping successfully.
Hi Rahul,
I am trying to configure multiple windows host as nagios monitoring it is not allowing . Please suggest on this
Is nrpe running under secure layer, Nagios, and NRPE communication is encrypted?
Hi!
Thanks for your tutorial, but why i can’t find the “check_nrpe”? I’m using Ubuntu Server 14.04 btw
Hope you can explain why ASAP
Thanks!
HI,
Check_nrpe command will be found on Nagios server. This command is part of nagios-nrpe-plugin package. Install it on your Nagios server.
i have downloaded nrpe pkg and installed it. so how can i restart it.
[root@Redhat-test ~]# service nrpe restart
nrpe: unrecognized service
Hello Brother,
My question is : How to add icon/image in front of host or services on nagios portal.
for example i have one host in nagios it is Windows 2008 i want to keep icon/image of M.S.Windows in front of host on nagios portal so that i can recognize easily.
how to do this process through nagios configurations ?
Thank you very much in advance.
[email protected]
-Jonus Joseph
Hi Joseph,
Edit you host configuration file and add below line under define host section.
define host {
——–
——–
icon_image windowsserver.png
}
Now update an icon image at DOCUMENTROOT/images/logos/ directory with name windowsserver.png. change DOCUMENTROOT with path of your nagios html directory.
I hope this will help you.