Puppet is an open-source, automation admin engine used to perform administrative tasks and server management remotely. This tool is available on Linux, Unix, and Windows. This configuration management tool will help you automate the management and configuration of your server infrastructure. After following this tutorial, you should have fully set up Puppet master and client nodes on your Ubuntu systems.
This tutorial help you to install and configure Puppet master and agent nodes on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux systems.
Prerequisites
You must have:
- Two or more running Ubuntu 20.04 systems, one for master and other clients.
- Shell access to all systems with sudo privileged account.
- All systems must be connected with each other over private or public network.
Step 1 – Configure Hosts
Puppet master and client nodes uses hostnames to communicate with each other. So its good to start with assigning a unique hostname for each node.
1. Login to the master and each client node one by one and edit /etc/hosts file:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
2. Add the following entries at the end of each hosts file:
10.132.14.239 puppetmaster puppet 10.132.14.240 puppetclient1 10.132.14.241 puppetclient2
Here:
- 10.132.14.239 is the IP address of the master node.
- 10.132.14.240 is the IP address of the client node.
- 10.132.14.242 is the IP address of another client node.
- Add more client nodes, you required
Save your file and close it. To save file with nano editor press Ctrl + X and then type Y and press Enter to save the change and close file.
Step 2 – Install Puppet Server (Master Node)
Now, login to the Master node with the shell access
3. Install latest Puppet debian package to configure PPA on the master node:
wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet7-release-focal.debsudo dpkg -i puppet7-release-focal.deb
4. Once you added the PPA, update Apt cache and install the Puppet server with the following command:
sudo apt updatesudo apt install puppetserver -y
5. After successfully installation of all the Puppet packages. Edit the puppet server file by using:
sudo nano /etc/default/puppetserver
The default puppet server file configured to use 2GB of memory. In case your server doesn’t have enough memory. Reduce the memory size to 1GB or any other value:
JAVA_ARGS="-Xms1g -Xmx1g -Djruby.logger.class=com.puppetlabs.jruby_utils.jruby.Slf4jLogger"
Save you changes and close puppetserver file. To save file with nano editor press Ctrl + X and then type Y to save the changes.
6. Next, start the Puppet service and set it to auto-start on system boot:
sudo systemctl start puppetserversudo systemctl enable puppetserver
7. Once service is started, verify the service status with:
sudo systemctl status puppetserver
You will see the service status as running.
Now, start with the configuration of all client node.
Step 3 – Install Puppet Agent (Client Node)
First of all, make sure you already have updated hosts file entries defines in step 1 in all client nodes.
8. Now, download and install latest Puppet debian package to configure PPA on your client node:
wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet7-release-focal.debsudo dpkg -i puppet7-release-focal.deb
9. Once you configured the PPA, Install the Puppet agent package on all client servers.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install puppet-agent -y
10. Once the packages installation finished. Edit the Puppet configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
Add the following entries to the end of the Puppet configuration file to define the Puppet master node details:
[main] certname = puppetclient1 server = puppetmaster
Save your file and close it.
11. Next, start the Puppet agent service on all the client nodes and set it to auto-start on system boot:
sudo systemctl start puppetsudo systemctl enable puppet
12. Once done, verify the Puppet agent service is running properly:
sudo systemctl status puppet
You should see a running status on all the agent systems
Step 4 – Sign the Puppet Agent Certificates
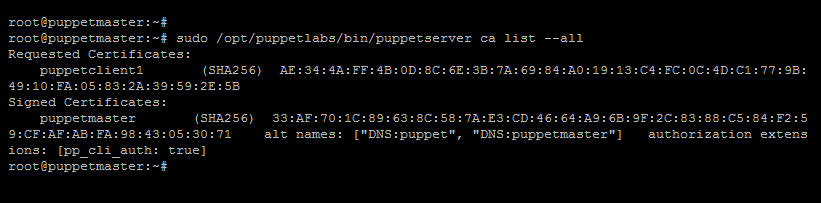
13. Your have done with the configuration’s. Now, login to the Puppet master node and run the following command to list all the available certificates:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca list --all
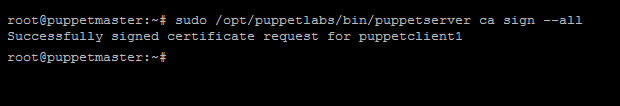
14. Next, sign all the clients certificates using:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca sign --all
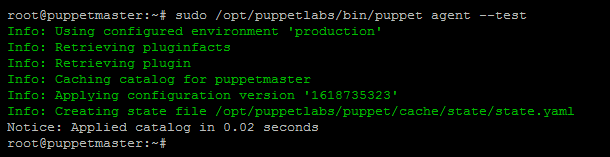
15. Finally, test the communication between Puppet master and client nodes using the following command.
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
Conclusion
That’s it. You have successfully installed Puppet on Ubuntu 20.04 system. This tutorial describes you to install Puppet on master node as well as on a client node.
You can also visit the official documentation for more about Puppet server node configuration and client node configuration on