An access modifier is a special kind of variable declaration that controls how and where other code can use the declared class, variable, or method. This blog will explain what access modifiers are and the three different levels of visibility for classes, methods, and variables with some practical examples.
Understanding the scope of your code is essential for writing readable and maintainable programs. Access modifiers are one way to achieve this goal. They tell other users of your code how you want them to interact with specific methods or variables. If you’re new to Java programming, these concepts may seem confusing at first glance; however, once you learn about them once or twice, they become much clearer. Keep reading to learn more about access modifiers in Java.
Access Modifiers in Java
Access modifiers are special keywords that let you specify how other code can interact with specific methods or variables within classes. Like many programming concepts, access modifiers are simple in practice but can seem confusing at first. Once you understand them, they can help make your code more readable and maintainable.
There are four different types of access modifiers in java:
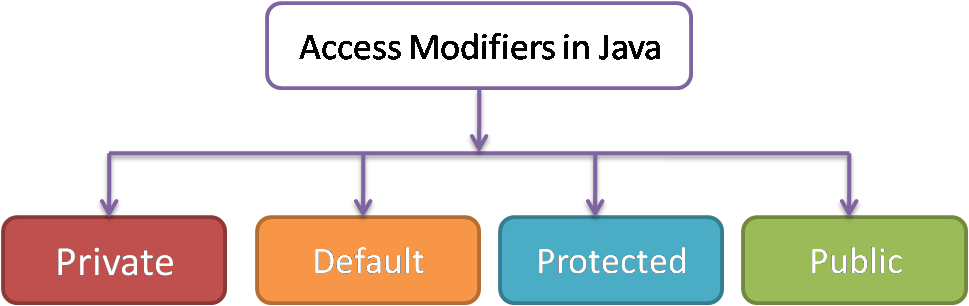
A Short Explanation:
- Private: A private member is accessible within the class scope.
- Default: A member with no access modifier is also known as package-private. Which is only accessible within classes in the same package.
- Protected: A protected member is accessible within all classes in the same package and the subclasses of the other packages.
- Public: A public member is accessible to anywhere.
Please see below infographic image to better understand the access level of different modifiers in Java.
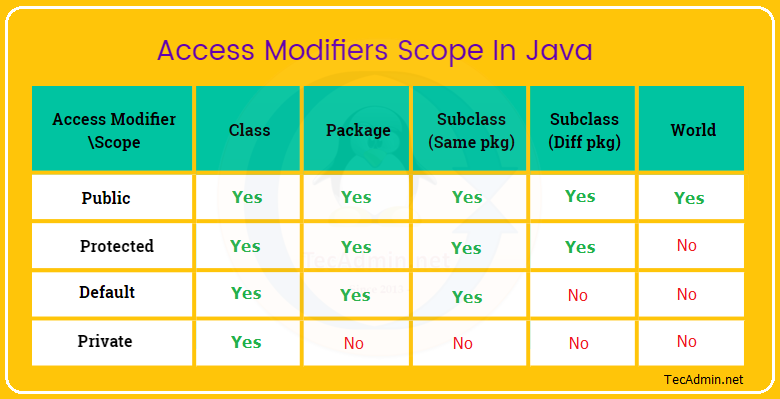
In the above representation, the fields with “Yes” are the allowed scope of modifiers. The “No” fields don’t allow accessibility of the member.
Private Access Modifier
A private access member is accessible within the class it is declared. A compile-time error will occur when another class tried to access it.
Let’s understand with an example: Created a class named “One”, and declare a private variable “i” with a default value. Now create a method showData() with default access in the same class that prints the variable value.
Now create another class “TecAdmin” with the main() method. Create an object of class One and try to print the variable “i”. As the variable “i” is declared private, the java compiler will through an error. Comment the above line and then call the showData method. This will print the value of “i” successfully as the method is also declared in the same class.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | class One{ private int i = 10; void showData(){ System.out.println(i); } } class TecAdmin{ public static void main(String args[]){ One obj = new One(); System.out.println(obj.i); //Compilation error // Comment above line to test the next line code obj.showData(); //Successfully run } } |
Conclusion
The main difference between each visibility level is who can access them: – public – everyone – private – only the class that contains the variable/method – protected – the class that contains the variable/method and any classes derived from it The visibility of the class, method, or variable determines if and how other methods or classes can interact with it. This is called encapsulation, and it’s one of the cornerstones of object-oriented programming. And now that you know what access modifiers are and how they work, you can use them in your own code to make it more readable and maintainable.