Welcome to our comprehensive guide on setting up Selenium with Python and Chrome Driver on Ubuntu. Selenium is a powerful tool for automating web browsers, and Python makes it easy to write scripts. In this guide, we’ll walk you through each step, from installing the necessary software to running your first automated test. Whether you’re new to programming or just new to Selenium, this guide is designed for beginners. By the end, you’ll have a working setup ready to automate your web tasks. Let’s get started on this exciting journey into web automation!
In this blog post, you will learn to set up a Selenium environment on an Ubuntu system. Also provides you with a few examples of Selenium scripts written in Python.
Prerequisites
You must have Sudo privileged account access to the Ubuntu system.
One of the examples also required a desktop environment to be installed.
Step 1: Installing Google Chrome
Use the below steps to install the latest Google Chrome browser on Ubuntu and Debian systems.
- First of all, download the latest Google Chrome Debian package on your system.
wget -nc https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb - Now, execute the following commands to install Google Chrome from the locally downloaded file.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install -f ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.debPress ‘y’ for all the confirmations asked by the installer.
This will complete the Google Chrome on your Ubuntu or Debian system. This will also create an Apt PPA file for further upgrades.
Step 2: Installing Selenium and Webdriver for Python
We will use a virtual environment for running Python scripts. Follow the below steps to create Python virtual environment and install the required python modules.
- Create a directory to store Python scripts. Then switch to the newly-created directory.
mkdir tests && cd tests - Set up the Python virtual environment and activate it.
python3 -m venv venvsource venv/bin/activateOnce the environment is activated, You will find the updated prompt as shown below screenshot:
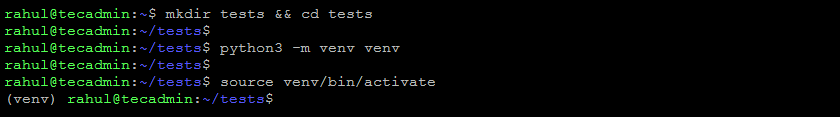
Create Python Environment for Selenium on Ubuntu - Now use PIP to install the selenium and webdriver-manager Python modules under the virtual environment.
pip install selenium webdriver-manager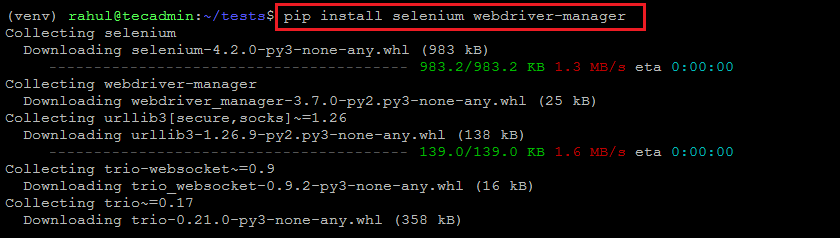
Installing Selenium and Webdriver Python Module on Ubuntu & Debian
Example 1: Selenium Python Script with Headless Chrome
Your system is ready to run Selenium scripts written in Python. Now, create a sample selenium script in Python that fetches the title of a website.
This script will run headless, So you can run it without an X desktop environment. You can simply SSH to your system and run the below example:
- Create a Python script and edit it in your favorite text editor:
nano test.py - Copy-paste the following Selenium Python script to the file.
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager options = Options() options.add_argument('--headless') options.add_argument('--no-sandbox') options.add_argument('--disable-dev-shm-usage') driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()), options=options) driver.get("https://python.org") print(driver.title) driver.close()Press
CTRL + Oto save content to the file and pressCTRL + Xto close the editor. - Now, run this Python script in a shell.
python test.pyYou will see the output something like the below:
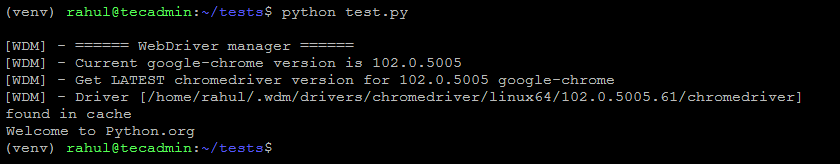
Running the Selenium Python Script
Example 2: Selenium Python Script with Chrome GUI
In order to run this example, the Ubuntu system must have installed a Desktop environment. If the desktop is not installed, use another tutorial to install the Desktop environment on Ubuntu systems.
Now, log in to the desktop interface and try to run the below example.
- Open a command prompt, then create a new Python script and edit it in your favorite text editor.
nano test.py - Copy-paste the below snippet in the file:
import time from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager options = Options() # options.add_argument('--headless') # options.add_argument('--no-sandbox') options.add_argument('--disable-dev-shm-usage') driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()), options=options) driver.get('http://www.google.com') search = driver.find_element(by=By.NAME, value="q") search.send_keys("Hey, Tecadmin") search.send_keys(Keys.RETURN) time.sleep(5) driver.close()Write the changes to file with
CTRL + Oand close this with keyboard shortcutCTRL + X - This is a Selenium script written in Python, that will launch the Google Chrome web browser and search for a defined string. then close the browser.
- Run the Python script in the terminal:
python test2.pyYou will see that a Browser window will open and perform the defined tasks in the script. See the below screencast of the run:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned about the configuration of Selenium for Python on Ubuntu and Debian Linux systems. Also provides you with two Selenium examples. Hope this tutorial helps you to understand to run Selenium with Python.


1 Comment
instead of using chrome, can use use opensource chromium ?