Subversion (SVN) is an open-source version control system. It helps you keep track of a collection of files and folders. Any time you change, add or delete a file or folder that you manage with Subversion, you commit these changes to your Subversion repository, which creates a new revision in your repository reflecting these changes. You can always go back, look at and get the contents of previous revisions.
This article will help you for step by step setup of subversion (svn) server on CentOS, Red Hat & Fedora systems.
Step 1 – Install Apache
Firstly, You need to install Apache web server to access svn server using HTTP URLs. Skip this step if you already have Apache web server on your system.
sudo yum install httpd# For CentOS/RHEL 7/6 sudo dnf install httpd# For CentOS/RHEL 9/8 & Fedora
Start Apache web server and setup to autostart on system boot
sudo systemctl restart httpdsudo systemctl enable httpd
Step 2 – Install Subversion
Use following command to install subversion packages and there dependencies. Also install svn module for Apache mod_dav_svn packages on your system..
sudo yum install subversion mod_dav_svn
Step 3 – Configure Subversion with Apache
Subversion module package creates an Apache configuration file, we just need to make necessary changes to it.
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.conf
LoadModule dav_svn_module modules/mod_dav_svn.so
LoadModule authz_svn_module modules/mod_authz_svn.so
Alias /svn /var/svn
<Location /svn>
DAV svn
SVNParentPath /var/svn
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Subversion User Authentication "
AuthUserFile /etc/svn-users
Require valid-user
</Location>
Step 4 – Create First SVN Repository
Use following command to create your fist svn repository.
cd /var/svnsvnadmin create myrepochown -R apache.apache myrepo
Step 5 – Create Users for Authenctication
Now add svn users in /etc/svn-users file. These users will use for authentication of svn repositories for checkout, commit processes. Following commands will add two users to /etc/svn-users file. I have created the file using touch command. This can be also created with -c switch in htpasswd command but remember that -c switch delete existing file and create a new file, So to avoid accidental removal of existing file we recommend to use touch command.
touch /etc/svn-usershtpasswd -m /etc/svn-users user1htpasswd -m /etc/svn-users user2
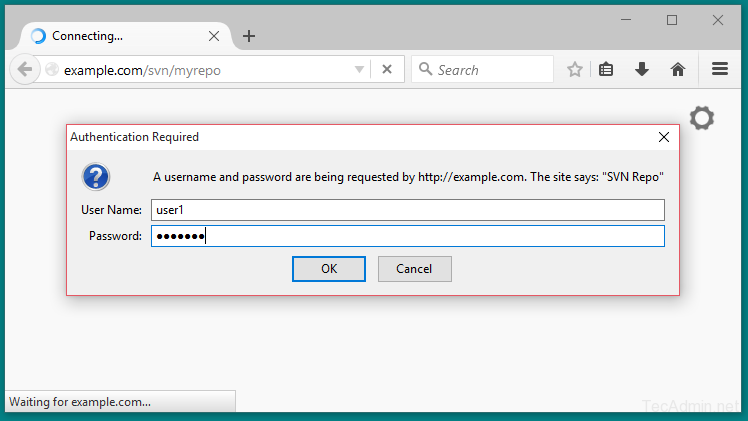
Step 6 – Access Repository in Browser
Use http urls to access your repository in browser. It will prompt for authentication. Use login credentials created in Step 5. Change example.com with your system host name, domain name or ip address.
http://example.com /svn/myrepo/
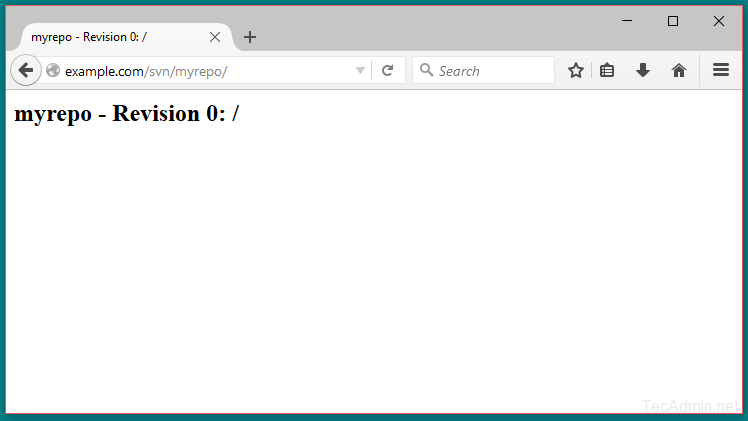
Step 7 – Basic Operations on Repository
This step is for testing that repository is working properly. Use following commands to add few files to your svn repository.
- Checkout repository on your local system. It will create the folder on local system with the repository name.
svn co http://example.com/svn/myrepo/ - Add some files to checkout repository directory.
cd myrepotouch file1.txt index.php - Now add newly created files to svn repository and commit them to svn server repository.
svn add file1.txt index.phpsvn ci file1.txt index.php -m "initial commit"
Let’s check back to
Conclusion
You have successfully set up an SVN server on your CentOS, Fedora and other RHEL-based systems. This server provides a robust platform for managing your development projects. Remember, it’s crucial to back up your repositories regularly and keep your system updated for security.
For more advanced configurations, such as setting up SSL, refer to the official Subversion documentation. Happy version controlling!
You may also like our next article How to Backup and Restore SVN Repository in Linux.



16 Comments
Hi, Thx, also had to remove alias to avoid “Redirect cycle detected for URL”
Hi Sir,
I followed the steps and went smooth, im creating mutiple repos under /var/www/svn/repo1..repo2 taking dump from another server.
I can login http://ip-address/svn/repo1 but i want to list the available repos under /svn.
http://ip-address/svn is showing Forbidden and server denies access.
Can you please help me on this.
Hi Rahul,
I have followed the steps as per the link https://tecadmin.net/install-svn-1-9-on-centos/ and from 3 step i have followed the current link (https://tecadmin.net/setup-subversion-server-on-centos/) when we try to access repo getting error as.
—-configuration file.——
/etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.conf
Alias /svn /opt/repo
DAV svn
SVNPath /opt/repo/devops
AuthType Basic
AuthName “SVN Repo”
#AuthUserFile /opt/WANdisco/apache22/conf/svn.passwd
AuthUserFile /etc/svn-users
AuthzSVNAccessFile /etc/svn_access_file
Require valid-user
—–error—-
Forbidden
You don’t have permission to access /svn/devops/ on this server.
Thanks
Sanjeev Kumar N
Hello sir,
Thanks.Ur tutorial is awesome, but can u pls add how to access the svn with LDAP users,.(Means needs to be integrate svn with LDAP)
Thanks
Thanks for the post, really helpful
for those who don’t wont to turn off selinux – remember to:
chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_rw_t /var/svn/*
I had to comment out the
Alias /svn /var/svn
(and bounce apache) to get rid of the errors:
svn: Repository moved permanently to ‘http://svn01/svn/scripts/’; please relocate”
from the svn command line client
You right with Alias /svn /var/svn in the conf. I get error svn: E195019: Redirect cycle detected for URL … when try to run the “svn co ” command . after comment it out the error disapperand the check out is done.
look at this url for more information:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/18474825/what-is-the-cause-of-svn-e195019-redirect-cycle-detected-for-url
Thanks for your help, i commented the same line and it fixed for me too.
I was unable to get authentication working using the above without also doing:
chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t [repo name]
(luckily this info was in the /etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.conf file or I’d likely be missing patches of hair)
Hi,
I have done as per article above, but I am not able to access it using http url. my http is configured to access at /home/user/public_html/
Now I have created a repo at /home/user/public_html/test
&
/var/www/svn/test1
but I am not able to access both..
what should be my value in step 3
SVNParentPath /var/www/svn
Thanks!
Hi Mukund,
What are you getting on http url and apache logs ?
I need to install apache svn on centOS but our data center is locked down so I can’t use yum or urls to install.
How do I do this manually?
I am trying to install SVN on Fedora 20 now. Both Fedora 20 and SVN are latest. I cannot find that subversion.conf file in your step 3. Anything wrong with the latest SVN and Fedora 20?
Wow that was superb !!
Thanks for the post
Very helpful thanks