MySQL is an relational database management system provide authentication mechanism to prevent unauthorized access. In MySQL, user management is an important aspect of database administration. Dropping unused or obsolete users can help improve security and optimize performance.
In this article, we will discuss how to drop a MySQL user using the command line interface.
Step 1: Connect to MySQL
The first step is to connect to the MySQL server using the command line interface. Open your terminal or command prompt and enter the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you to enter the root user’s password. After entering the correct password, you will be connected to the MySQL server.
Step 2: List existing users
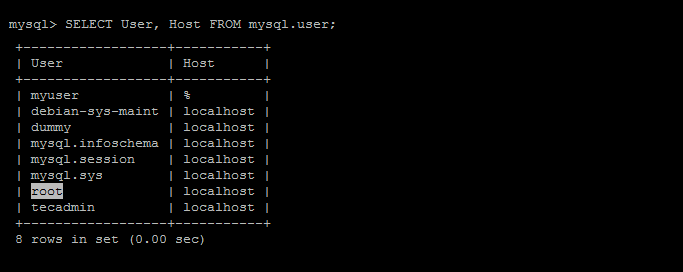
Before dropping a MySQL user, it’s a good practice to list all existing users to ensure that the user you want to drop actually exists. To list all users, enter the following command:
1 | SELECT User,Host FROM mysql.user; |
This will display a list of all existing MySQL users.
Step 3: Revoke privileges
Before dropping a MySQL user, it’s important to revoke any privileges associated with the user. This ensures that the user cannot access the database anymore. To revoke privileges, enter the following command:
1 | REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM 'user'@'localhost'; |
Replace ‘user’ with the username of the user you want to drop. The ‘localhost’ indicates the location from which the user can connect to the database. If the user can connect from multiple locations, you can use ‘%’ instead of ‘localhost’.
Step 4: Drop (Delete) user
After revoking privileges, you can drop the user using the following command:
1 | DROP USER 'user'@'localhost'; |
Replace ‘user’ with the username of the user you want to drop. The ‘localhost’ indicates the location from which the user can connect to the database.
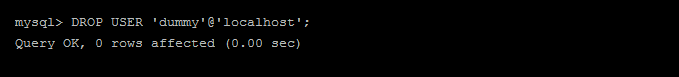
If the user can connect from multiple locations, you can use ‘%’ instead of ‘localhost’.
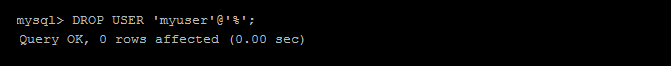
That’s it. Repeat the same command to remove more accounts no longer required.
Step 5: Verify user was dropped
To verify that the user was dropped successfully, you can list all existing users again using the same command from Step 2. The dropped user should no longer appear in the list.
Conclusion
Dropping unused or obsolete MySQL users can help improve security and optimize performance. In this article, we discussed how to drop a MySQL user using the command line interface. By following these steps, you can effectively manage MySQL users and ensure that only authorized users have access to your database.
