Systemd is a software application that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. It is the first service to initialize the boot sequence. This always runs with PID 1. This also helps us to manage system and application services on our Linux operating system.
We can also run any custom script as systemd service. It helps the script to start on system boot. This can be helpful for you to run any script which required to run at boot time only or to run always.
In our previous tutorial we have provides you instructions to run a Python script using Systemd. This tutorial covers running a shell script as a Systemd service.
Step 1 – Create a Shell Script
First of all, create a sample shell script, which needs to run at system startup. You can also create a shell script to run always using an infinite while loop. The script will keep running until the system goes down.
Create a shell script as per requirements. For testing purposes, I am creating a sample shell script as /usr/bin/script.sh.
sudo nano /usr/bin/script.sh
Added the following sample shell script code.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | #!/bin/bash while true do // Your statements go here sleep 10 done |
Press CTRL+O and hit enter to save changes. Then press CTRL + x to quit from nano editor.
Now, make the script executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/script.sh
To run a script once during system boot time doesn’t require any infinite loop. Instead of the above script, you can use your shell script to run as a Systemd service.
Step 2 – Create a Systemd Unit File
Next, create a service unit file for the systemd on your system. This file must have .service extension and saved under the under /lib/systemd/system/ directory
sudo nano /lib/systemd/system/shellscript.service
Now, add the following content and update the script filename and location. You can also change the description of the service.
[Unit] Description=My Shell Script [Service] ExecStart=/usr/bin/script.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file and close it.
Step 3 – Enable the New Service
Your system service has been added to your service. Let’s reload the systemctl daemon to read the new file. You need to reload this daemon each time after making any changes in .service file.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Now enable the service to start on system boot, also start the service using the following commands.
sudo systemctl enable shellscript.servicesudo systemctl start shellscript.service
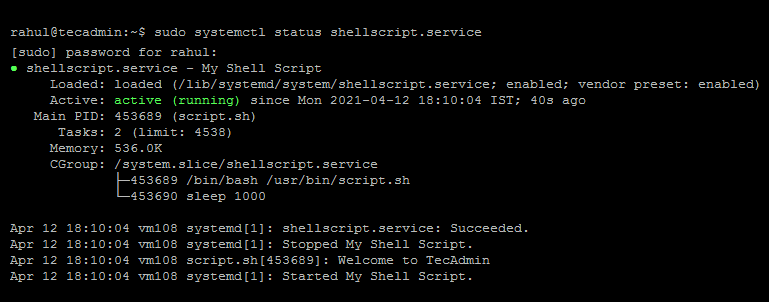
Finally verify the script is up and running as a systemd service.
sudo systemctl status shellscript.service
The output looks like the below:
All done!
Conclusion
Congratulation, You have successfully configured a shell script to run at system startup. This can be helpful to run your custom scripts that are required to start at system boot. This tutorial helped you to configure a shell script as systemd service.


6 Comments
many Thanks .. It is Awsum
This is useful material but you should place locally added services in /etc/systemd/system/
Other paths will work but the /usr/lib (or /lib) on is for the distribution package manager
https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.unit.html#Unit%20File%20Load%20Path
A minor detail but it’s always good to be as correct as possible when teaching other people.
Thanks you for this great tutorial
Thanks for the steps.. it really helped
can we write a shell script which automatically copies the information to the service file (shellscript.service ) automatically when we run the .sh file instead of us entering it manually ?
of course you can. but this isn’t a bash tutorial